The combination of olaparib and camptothecin for effective radiosensitization
- PMID: 22524618
- PMCID: PMC3430568
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-7-62
The combination of olaparib and camptothecin for effective radiosensitization
Abstract
Background: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) is a key enzyme involved in the repair of radiation-induced single-strand DNA breaks. PARP inhibitors such as olaparib (KU-0059436, AZD-2281) enhance tumor sensitivity to radiation and to topoisomerase I inhibitors like camptothecin (CPT). Olaparib is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of PARP-1 and PARP-2 that has been tested in multiple clinical trials. The purpose of this study was to investigate the characteristics of the sensitizing effect of olaparib for radiation and CPT in order to support clinical application of this agent.
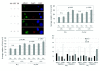
Methods: DLD-1 cells (a human colorectal cancer cell line) and H1299 cells (a non-small cell lung cancer cell line) with differences of p53 gene status were used. The survival of these cells was determined by clonogenic assay after treatment with drugs and X-ray irradiation. The γH2AX focus formation assay was performed to examine the influence of olaparib on induction and repair of double-stranded DNA breaks after exposure to radiation or CPT.
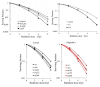
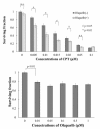
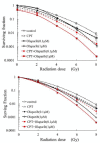
Results: A radiosensitizing effect of olaparib was seen even at 0.01 μM. Its radiosensitizing effect after exposure for 2 h was similar to that after 24 h. H1299 cells with depletion or mutation of p53 were more radioresistant than H1299 cells with wild-type p53. However, similar enhancement of radiosensitization by olaparib was observed with all of the tested cell lines regardless of the p53 status. Olaparib also sensitized cells to CPT. This sensitizing effect was seen at low concentrations of olaparib such as 0.01 μM, and its sensitizing effect was the same at both 0.01 μM and 1 μM. The combination of olaparib and CPT had a stronger radiosensitizing effect. The results of the γH2AX focus assay corresponded with the clonogenic assay findings.
Conclusion: Olaparib enhanced sensitivity to radiation and CPT at low concentrations and after relatively short exposure times such as 2 h. The radiosensitizing effect of olaprib was not dependent on the p53 status of tumor cells. These characteristics could be advantageous for clinical radiotherapy since tumor cells may be exposed to low concentrations of olaparib and/or may have different levels of p53 mutation. The combination of olaparib and CPT had a stronger radiosensitizing effect, indicating that combining a PARP inihibitor with a topoiomerase I inhibitor could be promising for clinical radiosensitization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PARP-1 inhibition with or without ionizing radiation confers reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxicity preferentially to cancer cells with mutant TP53.Oncogene. 2018 May;37(21):2793-2805. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0130-6. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29511347 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect and Mechanism of Radiosensitization of Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibitor n Lewis Cells and Xenografts].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016 Jan;19(1):16-23. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2016.01.02. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26805733 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Extent of radiosensitization by the PARP inhibitor olaparib depends on its dose, the radiation dose and the integrity of the homologous recombination pathway of tumor cells.Radiother Oncol. 2015 Sep;116(3):358-65. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2015.03.028. Epub 2015 May 13. Radiother Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25981132
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition as a model for synthetic lethality in developing radiation oncology targets.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2010 Oct;20(4):274-81. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2010.06.001. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20832020 Review.
-
[From poly(ADP-ribose) discovery to PARP inhibitors in cancer therapy].Bull Cancer. 2015 Oct;102(10):863-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2015.07.012. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Bull Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26384693 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Colorectal Cancer Develops Inherent Radiosensitivity That Can Be Predicted Using Patient-Derived Organoids.Cancer Res. 2022 Jun 15;82(12):2298-2312. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-4128. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35472075 Free PMC article.
-
Current concepts in clinical radiation oncology.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2014 Mar;53(1):1-29. doi: 10.1007/s00411-013-0497-2. Epub 2013 Oct 20. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2014. PMID: 24141602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome destabilization-associated phenotypes arising as a consequence of therapeutic treatment are suppressed by Olaparib.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 27;18(1):e0281168. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281168. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36706121 Free PMC article.
-
PARP-1 promotes autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR pathway in CNE-2 human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells following ionizing radiation, while inhibition of autophagy contributes to the radiation sensitization of CNE-2 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Aug;12(2):1868-76. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3604. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25872765 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer to 90Y and the radiobiological implications for radioembolisation therapy.Phys Med Biol. 2019 Jul 5;64(13):135018. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ab23c4. Phys Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31117062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hall EJ. In: Radiobiology for the radiologist, ed. 6. Hall EJ, Giaccia AM, editor. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia; 2006. DNA strand breaks and chromosomal aberrations; pp. 16–29.
-
- Saleh-Gohari N, Bryant HE, Schultz N, Parker KM, Cassel T, Helleday T. Spontaneous homologous recombination is induced by collapsed replication forks that are caused by ebdogenous DNA single-strand breaks. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(16):7158–7169. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.16.7158-7169.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caldecott KW. Protein-protein inetractions during mammalian DNA single-strand break repair. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:247–251. - PubMed
-
- Chalmers AJ. The potential role and application of PARP inhibitors in cancer treatment. Brit Med Bull. 2009;89:23–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

