Regulation of MntH by a dual Mn(II)- and Fe(II)-dependent transcriptional repressor (DR2539) in Deinococcus radiodurans
- PMID: 22523570
- PMCID: PMC3327659
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035057
Regulation of MntH by a dual Mn(II)- and Fe(II)-dependent transcriptional repressor (DR2539) in Deinococcus radiodurans
Abstract
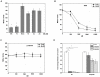
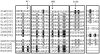
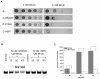
The high intracellular Mn/Fe ratio observed within the bacteria Deinococcus radiodurans may contribute to its remarkable resistance to environmental stresses. We isolated DR2539, a novel regulator of intracellular Mn/Fe homeostasis in D. radiodurans. Electrophoretic gel mobility shift assays (EMSAs) revealed that DR2539 binds specifically to the promoter of the manganese acquisition transporter (MntH) gene, and that DR0865, the only Fur homologue in D. radiodurans, cannot bind to the promoter of mntH, but it can bind to the promoter of another manganese acquisition transporter, MntABC. β-galactosidase expression analysis indicated that DR2539 acts as a manganese- and iron-dependent transcriptional repressor. Further sequence alignment analysis revealed that DR2539 has evolved some special characteristics. Site-directed mutagenesis suggested that His98 plays an important role in the activities of DR2539, and further protein-DNA binding activity assays showed that the activity of H98Y mutants decreased dramatically relative to wild type DR2539. Our study suggests that D. radiodurans has evolved a very efficient manganese regulation mechanism that involves its high intracellular Mn/Fe ratio and permits resistance to extreme conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Mur regulator protein in the extremophilic bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 22;9(9):e106341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106341. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25243898 Free PMC article.
-
DR2539 is a novel DtxR-like regulator of Mn/Fe ion homeostasis and antioxidant enzyme in Deinococcus radiodurans.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 May 28;396(2):413-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.106. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20417183
-
Dual repression by Fe(2+)-Fur and Mn(2+)-MntR of the mntH gene, encoding an NRAMP-like Mn(2+) transporter in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2001 Aug;183(16):4806-13. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.16.4806-4813.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11466284 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidative system of Deinococcus radiodurans.Res Microbiol. 2020 Mar;171(2):45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2019.11.002. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Res Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31756434 Review.
-
How radiation kills cells: survival of Deinococcus radiodurans and Shewanella oneidensis under oxidative stress.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005 Apr;29(2):361-75. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2004.12.007. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15808748 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular dGMP enhances Deinococcus radiodurans tolerance to oxidative stress.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054420. Epub 2013 Jan 24. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23365666 Free PMC article.
-
A Mur regulator protein in the extremophilic bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 22;9(9):e106341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106341. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25243898 Free PMC article.
-
Development of novel Escherichia coli cell-based biosensors to monitor Mn(II) in environmental systems.Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 19;13:1051926. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1051926. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36601404 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of bacterial diversity associated with deep sea ferromanganese nodules from the South China Sea.J Microbiol. 2015 Sep;53(9):598-605. doi: 10.1007/s12275-015-5217-y. Epub 2015 Aug 27. J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26310303
-
High-quality genome sequence of the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus ficus KS 0460.Stand Genomic Sci. 2017 Jul 28;12:46. doi: 10.1186/s40793-017-0258-y. eCollection 2017. Stand Genomic Sci. 2017. PMID: 28775794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Battista JR, Earl AM, Park MJ. Why is Deinococcus radiodurans so resistant to ionizing radiation? Trends Microbiol. 1999;7:362–365. - PubMed
-
- Rainey FA, Nobre MF, Schumann P, Stackebrandt E, da Costa MS. Phylogenetic diversity of the deinococci as determined by 16S ribosomal DNA sequence comparison. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1997;47:510–514. - PubMed
-
- Daly MJ. Death by protein damage in irradiated cells. DNA Repair (Amst) 2011;11:12–21. - PubMed
-
- Hua Y, Narumi I, Gao G, Tian B, Satoh K, et al. PprI: a general switch responsible for extreme radioresistance of Deinococcus radiodurans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;306:354–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

