Membrane lipid raft organization is uniquely modified by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
- PMID: 22515942
- PMCID: PMC3404206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plefa.2012.03.008
Membrane lipid raft organization is uniquely modified by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
Abstract
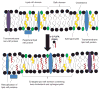
Fish oil, enriched in bioactive n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), has been shown to play a role in prevention of colon cancer. The effects of n-3 PUFA are pleiotropic and multifaceted, resulting in an incomplete understanding of their molecular mechanisms of action. Here, we focus on a highly conserved mechanism of n-3 PUFA, which is the alteration of the organization of the plasma membrane. We highlight recent work demonstrating that enrichment of n-3 PUFA in the plasma membrane alters the lateral organization of membrane signaling assemblies (i.e. lipid rafts). This mechanism is central for n-3 PUFA regulation of downstream signaling, T-cell activation, transcriptional activation, and cytokine secretion. We conclude that these studies provide strong evidence for a predominant mechanism by which n-3 PUFA function in colon cancer prevention.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biophysical and biochemical mechanisms by which dietary N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids from fish oil disrupt membrane lipid rafts.J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Feb;23(2):101-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Dec 1. J Nutr Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22137258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Lipid Microclusters, and Vitamin E.Curr Top Membr. 2015;75:209-31. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Curr Top Membr. 2015. PMID: 26015284 Review.
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids exert immunomodulatory effects on lymphocytes by targeting plasma membrane molecular organization.Mol Aspects Med. 2012 Feb;33(1):46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2011.10.002. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Mol Aspects Med. 2012. PMID: 22020145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Models of plasma membrane organization can be applied to mitochondrial membranes to target human health and disease with polyunsaturated fatty acids.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013 Jan;88(1):21-5. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2012.03.004. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013. PMID: 22464052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids attenuate hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by modulating toll-like receptor recruitment into lipid rafts.Clin Nutr. 2013 Oct;32(5):855-62. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2012.11.026. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Clin Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23395256
Cited by
-
Heterogeneous Distribution of Phospholipid Molecular Species in the Surface Culture of Flammulina velutipes: New Facts about Lipids Containing α-Linolenic Fatty Acid.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;9(1):102. doi: 10.3390/jof9010102. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36675923 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Docosahexaenoic Acid as a Potential Treatment for Semi-acute and Chronic Particle-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation in Balb/c Mice.Inflammation. 2022 Apr;45(2):677-694. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01576-y. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Inflammation. 2022. PMID: 34655011 Free PMC article.
-
All n-3 PUFA are not the same: MD simulations reveal differences in membrane organization for EPA, DHA and DPA.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018 May;1860(5):1125-1134. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 29305832 Free PMC article.
-
Change in Blood and Benign Breast Biomarkers in Women Undergoing a Weight-Loss Intervention Randomized to High-Dose ω-3 Fatty Acids versus Placebo.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2021 Sep;14(9):893-904. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-20-0656. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2021. PMID: 34244155 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Docosahexaenoic Acid, a Key Compound for Enhancing Sensitization to Drug in Doxorubicin-Resistant MCF-7 Cell Line.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 29;15(7):1658. doi: 10.3390/nu15071658. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Martínez ME, Jacobs ET. Diet and Environment, Role in Colon Cancer. In: Leonard J, editor. Encyclopedia of Gastroenterology. Elsevier; New York: 2004. pp. 593–597.
-
- Anti M, Armelao F, Marra G, et al. Effects of different doses of fish oil on rectal cell proliferation in patients with sporadic colonic adenomas. Gastroenterology. 1994;107:1709–1718. - PubMed
-
- Anti M, Marra G, Armelao F, Bartoli GM, et al. Effect of omega-3 fatty acids on rectal mucosal cell proliferation in subjects at risk for colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 1992;103:883–891. - PubMed
-
- Bartram HP, Gostner A, Scheppach W, et al. Effects of fish oil on rectal cell proliferation, mucosal fatty acids, and prostaglandin E2 release in healthy subjects. Gastroenterology. 1993;105:1317–1322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

