Is histone acetylation the most important physiological function for CBP and p300?
- PMID: 22511639
- PMCID: PMC3371760
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100453
Is histone acetylation the most important physiological function for CBP and p300?
Abstract
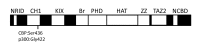
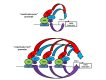
Protein lysine acetyltransferases (HATs or PATs) acetylate histones and other proteins, and are principally modeled as transcriptional coactivators. CREB binding protein (CBP, CREBBP) and its paralog p300 (EP300) constitute the KAT3 family of HATs in mammals, which has mostly unique sequence identity compared to other HAT families. Although studies in yeast show that many histone mutations cause modest or specific phenotypes, similar studies are impractical in mammals and it remains uncertain if histone acetylation is the primary physiological function for CBP/p300. Nonetheless, CBP and p300 mutations in humans and mice show that these coactivators have important roles in development, physiology, and disease, possibly because CBP and p300 act as network "hubs" with more than 400 described protein interaction partners. Analysis of CBP and p300 mutant mouse fibroblasts reveals CBP/p300 are together chiefly responsible for the global acetylation of histone H3 residues K18 and K27, and contribute to other locus-specific histone acetylation events. CBP/p300 can also be important for transcription, but the recruitment of CBP/p300 and their associated histone acetylation marks do not absolutely correlate with a requirement for gene activation. Rather, it appears that target gene context (e.g. DNA sequence) influences the extent to which CBP and p300 are necessary for transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Target gene context influences the transcriptional requirement for the KAT3 family of CBP and p300 histone acetyltransferases.Epigenetics. 2010 Jan 1;5(1):9-15. doi: 10.4161/epi.5.1.10449. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Epigenetics. 2010. PMID: 20110770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic acetylation of all lysine-4 trimethylated histone H3 is evolutionarily conserved and mediated by p300/CBP.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 10;108(19):7814-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100099108. Epub 2011 Apr 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21518915 Free PMC article.
-
Acetyltransferases CBP/p300 Control Transcriptional Switch of β-Catenin and Stat1 Promoting Osteoblast Differentiation.J Bone Miner Res. 2023 Dec;38(12):1885-1899. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4925. Epub 2023 Nov 7. J Bone Miner Res. 2023. PMID: 37850815
-
CBP/p300 double null cells reveal effect of coactivator level and diversity on CREB transactivation.EMBO J. 2010 Nov 3;29(21):3660-72. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.235. Epub 2010 Sep 21. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20859256 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and chemistry of the p300/CBP and Rtt109 histone acetyltransferases: implications for histone acetyltransferase evolution and function.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Dec;18(6):741-7. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.09.004. Epub 2008 Oct 27. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 18845255 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Tug of War: Pseudorabies Virus and Host Antiviral Innate Immunity.Viruses. 2022 Mar 6;14(3):547. doi: 10.3390/v14030547. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p300 Mediates Muscle Wasting in Lewis Lung Carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2019 Apr 1;79(7):1331-1342. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1653. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30705122 Free PMC article.
-
Shifting transcriptional machinery is required for long-term memory maintenance and modification in Drosophila mushroom bodies.Nat Commun. 2016 Nov 14;7:13471. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13471. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27841260 Free PMC article.
-
Linking functions: an additional role for an intrinsically disordered linker domain in the transcriptional coactivator CBP.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 5;7(1):4676. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04611-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28680062 Free PMC article.
-
Phospho-ΔNp63α/microRNA feedback regulation in squamous carcinoma cells upon cisplatin exposure.Cell Cycle. 2013 Feb 15;12(4):684-97. doi: 10.4161/cc.23598. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23343772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li B, Carey M, Workman JL. The role of chromatin during transcription. Cell. 2007;128:707–719. - PubMed
-
- Schwartzentruber J, Korshunov A, Liu XY, Jones DT, Pfaff E, Jacob K, Sturm D, Fontebasso AM, Quang DA, Tonjes M, Hovestadt V, Albrecht S, Kool M, et al. Driver mutations in histone H3.3 and chromatin remodelling genes in paediatric glioblastoma. Nature. 2012;482:226–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

