Deregulation of CREB signaling pathway induced by chronic hyperglycemia downregulates NeuroD transcription
- PMID: 22509362
- PMCID: PMC3318007
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034860
Deregulation of CREB signaling pathway induced by chronic hyperglycemia downregulates NeuroD transcription
Abstract
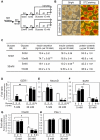
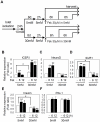
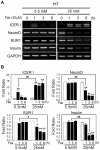
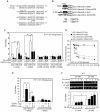
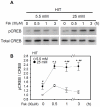
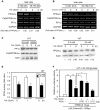
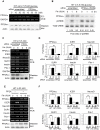
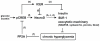
CREB mediates the transcriptional effects of glucose and incretin hormones in insulin-target cells and insulin-producing β-cells. Although the inhibition of CREB activity is known to decrease the β-cell mass, it is still unknown what factors inversely alter the CREB signaling pathway in β-cells. Here, we show that β-cell dysfunctions occurring in chronic hyperglycemia are not caused by simple inhibition of CREB activity but rather by the persistent activation of CREB due to decreases in protein phophatase PP2A. When freshly isolated rat pancreatic islets were chronically exposed to 25 mM (high) glucose, the PP2A activity was reduced with a concomitant increase in active pCREB. Brief challenges with 15 mM glucose or 30 µM forskolin after 2 hour fasting further increased the level of pCREB and consequently induced the persistent expression of ICER. The excessively produced ICER was sufficient to repress the transcription of NeuroD, insulin, and SUR1 genes. In contrast, when islets were grown in 5 mM (low) glucose, CREB was transiently activated in response to glucose or forskolin stimuli. Thus, ICER expression was transient and insufficient to repress those target genes. Importantly, overexpression of PP2A reversed the adverse effects of chronic hyperglycemia and successfully restored the transient activation of CREB and ICER. Conversely, depletion of PP2A with siRNA was sufficient to disrupt the negative feedback regulation of CREB and induce hyperglycemic phenotypes even under low glucose conditions. Our findings suggest that the failure of the negative feedback regulation of CREB is the primary cause for β-cell dysfunctions under conditions of pathogenic hyperglycemia, and PP2A can be a novel target for future therapies aiming to protect β-cells mass in the late transitional phase of non-insulin dependent type 2 diabetes (NIDDM).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles and regulation of the transcription factor CREB in pancreatic β -cells.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Nov;4(3):187-95. doi: 10.2174/1874467211104030187. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21488836 Review.
-
ERK1 is dispensable for mouse pancreatic beta cell function but is necessary for glucose-induced full activation of MSK1 and CREB.Diabetologia. 2017 Oct;60(10):1999-2010. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4356-6. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Diabetologia. 2017. PMID: 28721437
-
PPAR-γ activation increases insulin secretion through the up-regulation of the free fatty acid receptor GPR40 in pancreatic β-cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e50128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050128. Epub 2013 Jan 23. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23372643 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of membrane depolarisation-induced transcriptional activity of cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB) by the dual-leucine-zipper-bearing kinase in a pancreatic islet beta cell line.Diabetologia. 2006 Feb;49(2):332-42. doi: 10.1007/s00125-005-0087-1. Epub 2005 Dec 21. Diabetologia. 2006. PMID: 16369771
-
Potential roles of PP2A-Rac1 signaling axis in pancreatic β-cell dysfunction under metabolic stress: Progress and promise.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;180:114138. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114138. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32634437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription control pathways decode patterned synaptic inputs into diverse mRNA expression profiles.PLoS One. 2014 May 1;9(5):e95154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095154. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24787753 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis by extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields.Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Jun;49(3):1472-86. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8650-8. Epub 2014 Feb 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24532268
-
A Periodic Diet that Mimics Fasting Promotes Multi-System Regeneration, Enhanced Cognitive Performance, and Healthspan.Cell Metab. 2015 Jul 7;22(1):86-99. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.05.012. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Cell Metab. 2015. PMID: 26094889 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Defective fasting-induced PKA activation impairs adipose tissue glycogen degradation in obese Zucker rats.Int J Obes (Lond). 2020 Feb;44(2):500-509. doi: 10.1038/s41366-019-0327-y. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Int J Obes (Lond). 2020. PMID: 30705392
-
Decompensation of β-cells in diabetes: when pancreatic β-cells are on ICE(R).J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:768024. doi: 10.1155/2014/768024. Epub 2014 Feb 10. J Diabetes Res. 2014. PMID: 24672804 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jonas JC, Bensellam M, Duprez J, Elouil H, Guiot Y, et al. Glucose regulation of islet stress responses and beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009;11:65–81. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti SK, Mirmira RG. Transcription factors direct the development and function of pancreatic β cells. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003;14:78–84. - PubMed
-
- Habener JF, Kemp DM, Thomas MK. Minireview : Transcriptional regulation in pancreatic development. Endocrinol. 2005;146:1025–1034. - PubMed
-
- Naya FJ, Stellrecht CM, Tsai MJ. Tissue-specific regulation of the insulin gene by a novel basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1009–1919. - PubMed
-
- Kim JW, Seghers V, Cho JH, Kang Y, Kim S, et al. Transactivation of the mouse sulfonylurea receptor I gene by BETA2/NeuroD. Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:1097–1107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

