Curcumin inhibits tumor proliferation induced by neutrophil elastase through the upregulation of α1-antitrypsin in lung cancer
- PMID: 22507634
- PMCID: PMC5528353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2012.03.005
Curcumin inhibits tumor proliferation induced by neutrophil elastase through the upregulation of α1-antitrypsin in lung cancer
Abstract
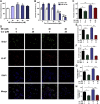
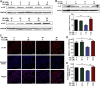
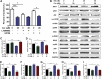
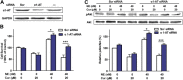
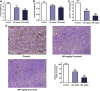
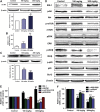
Lung carcinogenesis is a complex process in an unregulated inflammatory environment. Curcumin has been extensively investigated as a multi-target anti-tumor and anti-inflammation compound. In this paper, we demonstrate a novel inflammation-related mechanism for curcumin-induced inhibition of lung tumor growth. We found that neutrophil elastase, an important regulator of inflammatory processes, directly triggered tumor cell proliferation in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells, and curcumin could completely suppress the excess tumor proliferation induced by neutrophil elastase. α1-antitrypsin is synthesized by tumor cells and is the natural inhibitor of neutrophil elastase. We found that curcumin counteracted the decrease of α1-antitrypsin induced by neutrophil elastase by inducing the promoter activity of α1-antitrypsin and promoting its expression in A549 cells. The inhibition of neutrophil elastase-induced proliferation by curcumin was dependent on the PI3K/Akt pathway. Knockdown of α1-antitrypsin by siRNA further enhanced the tumor cell proliferation induced by neutrophil elastase and significantly blocked the anti-proliferation effect of curcumin against neutrophil elastase. Curcumin remarkably inhibited the primary tumor growth of Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) in C57BL/6 mice. We further showed that curcumin upregulated the level of α1-antitrypsin in primary tumor tissue by promoting its local expression, and the protein level of neutrophil elastase in tumor tissue was obviously decreased in mice treated with curcumin. Overall, our results suggest that neutrophil elastase and α1-antitrypsin play important roles in modulating lung tumor proliferation in inflammatory microenvironment and curcumin inhibits neutrophil elastase-induced tumor proliferation via upregulating α1-antitrypsin expression in vitro and in vivo.
Copyright © 2012 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EGCG reverses human neutrophil elastase-induced migration in A549 cells by directly binding to HNE and by regulating α1-AT.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 16;5:11494. doi: 10.1038/srep11494. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26177797 Free PMC article.
-
Local regulation of neutrophil elastase activity by endogenous α1-antitrypsin in lipopolysaccharide-primed hematological cells.Thromb Res. 2011 Sep;128(3):283-92. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.04.024. Epub 2011 May 31. Thromb Res. 2011. PMID: 21624645
-
Curcumin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer cells through the upregulation of miR-192-5p and suppression of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2015 Nov;34(5):2782-9. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4258. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26351877
-
Role of imbalance between neutrophil elastase and alpha 1-antitrypsin in cancer development and progression.Lancet Oncol. 2004 Mar;5(3):182-90. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(04)01414-7. Lancet Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15003202 Review.
-
Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency and asthma.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021 Feb 1;21(1):46-51. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000711. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33284159 Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin induces apoptosis of HepG2 cells via inhibiting fatty acid synthase.Target Oncol. 2014 Sep;9(3):279-86. doi: 10.1007/s11523-013-0286-5. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Target Oncol. 2014. PMID: 23821378
-
Curcumin combined with glycyrrhetinic acid inhibits the development of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by down-regulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway.Am J Transl Res. 2017 Dec 15;9(12):5567-5575. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 29312508 Free PMC article.
-
miR-151a enhances Slug dependent angiogenesis.Oncotarget. 2020 Jun 9;11(23):2160-2171. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27331. eCollection 2020 Jun 9. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 32577162 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting neutrophil elastase is a promising direction for future cancer treatment.Discov Oncol. 2024 May 15;15(1):167. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01010-3. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38750338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin Regulates Cancer Progression: Focus on ncRNAs and Molecular Signaling Pathways.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 12;11:660712. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.660712. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33912467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cadranel, J. , Bellocq, A. , Antoine, M. , Flahault, A. , Philippe, C. , Crestani, B. , Bernaudin, J.F. , Mayaud, C. , Milleron, B. , Baud, L. , 1998. Neutrophil alveolitis in bronchioloalveolar carcinoma – induction by tumor-derived interleukin-8 and relation to clinical outcome. Am. J. Pathol.. 152, 83–92. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng, A.L. , Hsu, C.H. , Lin, J.K. , Hsu, M.M. , Ho, Y.F. , Shen, T.S. , Ko, J.Y. , Lin, J.T. , Lin, B.R. , Ming-Shiang, W. , Yu, H.S. , Jee, S.H. , Chen, G.S. , Chen, T.M. , Chen, C.A. , Lai, M.K. , Pu, Y.S. , Pan, M.H. , Wang, Y.J. , Tsai, C.C. , Hsieh, C.Y. , 2001. Phase I clinical trial of curcumin, a chemopreventive agent, in patients with high-risk or pre-malignant lesions. Anticancer Res.. 21, 2895–2900. - PubMed
-
- Choi, B.H. , Kim, C.G. , Lim, Y. , Shin, S.Y. , Lee, Y.H. , 2008. Curcumin down-regulates the multidrug-resistance mdr1b gene by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF kappa B pathway. Cancer Lett.. 259, 111–118. - PubMed
-
- El-Akawi, Z.J. , Abu-Awad, A.M. , Sharara, A.M. , Khader, Y. , 2010. The importance of alpha-1 antitrypsin (alpha1-AT) and neopterin serum levels in the evaluation of non-small cell lung and prostate cancer patients. Neuroendocrinol. Lett.. 31, 113–116. - PubMed
-
- El-Rayes, B.F. , Ali, S. , Ali, I.F. , Philip, P.A. , Abbruzzese, J. , Sarkar, F.H. , 2006. Potentiation of the effect of erlotinib by genistein in pancreatic cancer: the role of Akt and nuclear factor-kappaB. Cancer Res.. 66, 10553–10559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

