Impaired inflammatory responses in murine Lrrk2-knockdown brain microglia
- PMID: 22496842
- PMCID: PMC3322140
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034693
Impaired inflammatory responses in murine Lrrk2-knockdown brain microglia
Abstract
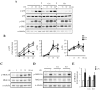
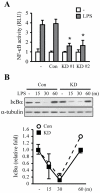
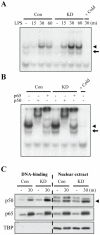
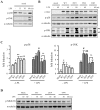
LRRK2, a Parkinson's disease associated gene, is highly expressed in microglia in addition to neurons; however, its function in microglia has not been evaluated. Using Lrrk2 knockdown (Lrrk2-KD) murine microglia prepared by lentiviral-mediated transfer of Lrrk2-specific small inhibitory hairpin RNA (shRNA), we found that Lrrk2 deficiency attenuated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced mRNA and/or protein expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6. LPS-induced phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and stimulation of NF-κB-responsive luciferase reporter activity was also decreased in Lrrk2-KD cells. Interestingly, the decrease in NF-κB transcriptional activity measured by luciferase assays appeared to reflect increased binding of the inhibitory NF-κB homodimer, p50/p50, to DNA. In LPS-responsive HEK293T cells, overexpression of the human LRRK2 pathologic, kinase-active mutant G2019S increased basal and LPS-induced levels of phosphorylated p38 and JNK, whereas wild-type and other pathologic (R1441C and G2385R) or artificial kinase-dead (D1994A) LRRK2 mutants either enhanced or did not change basal and LPS-induced p38 and JNK phosphorylation levels. However, wild-type LRRK2 and all LRRK2 mutant variants equally enhanced NF-κB transcriptional activity. Taken together, these results suggest that LRRK2 is a positive regulator of inflammation in murine microglia, and LRRK2 mutations may alter the microenvironment of the brain to favor neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Euscaphic acid isolated from roots of Rosa rugosa inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses via TLR4-mediated NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Cell Biochem. 2012 Jun;113(6):1936-46. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24062. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22234926
-
Resveratrol inhibits inflammatory responses via the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in cultured LPS-stimulated microglial cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032195. Epub 2012 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363816 Free PMC article.
-
Lutein suppresses inflammatory responses through Nrf2 activation and NF-κB inactivation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV-2 microglia.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015 Sep;59(9):1663-73. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500109. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015. PMID: 26016441
-
Curcumin Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Activated Neuroinflammation via Modulation of miR-199b-5p/IκB Kinase β (IKKβ)/Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) Pathway in Microglia.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Dec 21;25:9801-9810. doi: 10.12659/MSM.918237. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31862869 Free PMC article.
-
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 positively regulates inflammation and down-regulates NF-κB p50 signaling in cultured microglia cells.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Dec 9;12:230. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0449-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26646749 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulation of α-synuclein homeostasis and inflammasome activation by microglial autophagy.Sci Adv. 2022 Oct 28;8(43):eabn1298. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn1298. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36288297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf2/Wnt resilience orchestrates rejuvenation of glia-neuron dialogue in Parkinson's disease.Redox Biol. 2020 Sep;36:101664. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101664. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32863224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LRRK2 Contributes to Secondary Brain Injury Through a p38/Drosha Signaling Pathway After Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Mar 1;12:51. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00051. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29545743 Free PMC article.
-
Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 Controls the Ca2+/Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells/IL-2 Pathway during Aspergillus Non-Canonical Autophagy in Dendritic Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 8;9:210. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00210. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29472933 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Imaging of Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's Disease: Recent Advancements.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 15;9:655819. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.655819. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34336822 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang L, Guo JF, Nie LL, Xu Q, Zuo X, et al. A novel LRRK2 mutation in a mainland Chinese patient with familial Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 2010;468:198–201. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y, Liu Y, Wu Q, Hong H, Zhou H, et al. Confirmation of LRRK2 S1647T variant as a risk factor for Parkinson's disease in Southern China. Eur J Neurol 2010 - PubMed
-
- West AB, Moore DJ, Choi C, Andrabi SA, Li X, et al. Parkinson's disease-associated mutations in LRRK2 link enhanced GTP-binding and kinase activities to neuronal toxicity. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:223–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

