Proteomic profiling of EBNA1-host protein interactions in latent and lytic Epstein-Barr virus infections
- PMID: 22496234
- PMCID: PMC3393576
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00194-12
Proteomic profiling of EBNA1-host protein interactions in latent and lytic Epstein-Barr virus infections
Erratum in
-
Correction for Malik-Soni and Frappier, Proteomic Profiling of EBNA1-Host Protein Interactions in Latent and Lytic Epstein-Barr Virus Infections.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(17):9143. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01581-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26240277 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
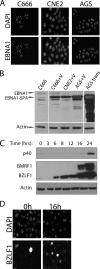
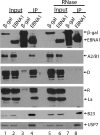
The Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) protein of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is expressed in both latent and lytic modes of EBV infection and contributes to EBV-associated cancers. Using a proteomics approach, we profiled EBNA1-host protein interactions in nasopharyngeal and gastric carcinoma cells in the context of latent and lytic EBV infection. We identified several interactions that occur in both modes of infection, including a previously unreported interaction with nucleophosmin and RNA-mediated interactions with several heterogeneous ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) and La protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Carcinoma-risk variant of EBNA1 deregulates Epstein-Barr Virus episomal latency.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7248-7264. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14540. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28077791 Free PMC article.
-
EBNA1.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:3-34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_1. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428370 Review.
-
Potential cellular functions of Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 (EBNA1) of Epstein-Barr Virus.Viruses. 2013 Jan 16;5(1):226-40. doi: 10.3390/v5010226. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23325328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma through disruption of PML nuclear bodies.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Oct 3;4(10):e1000170. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000170. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18833293 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of the Epstein-Barr virus EBNA1 protein to gastric carcinoma.J Virol. 2012 Jan;86(1):60-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05623-11. Epub 2011 Oct 19. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22013060 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent genes.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Jan 23;47(1):e131. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.84. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25613728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of MEF2B, EBF1, and IL6R as Direct Gene Targets of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Nuclear Antigen 1 Critical for EBV-Infected B-Lymphocyte Survival.J Virol. 2015 Oct 14;90(1):345-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02318-15. Print 2016 Jan 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26468528 Free PMC article.
-
A proteomic approach to discover and compare interacting partners of papillomavirus E2 proteins from diverse phylogenetic groups.Proteomics. 2015 Jun;15(12):2038-50. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400613. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25758368 Free PMC article.
-
Awakening the sleeping giant: Epstein-Barr virus reactivation by biological agents.Pathog Dis. 2024 Feb 7;82:ftae002. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftae002. Pathog Dis. 2024. PMID: 38281067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of ARKL1 as a Negative Regulator of Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation.J Virol. 2019 Sep 30;93(20):e00989-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00989-19. Print 2019 Oct 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31341047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen GI, Gingras AC. 2007. Affinity-purification mass spectrometry (AP-MS) of serine/threonine phosphatases. Methods 42:298–305 - PubMed
-
- Chen MR, Yang JF, Wu CW, Middeldorp JM, Chen JY. 1998. Physical association between the EBV protein EBNA-1 and P32/TAP/hyaluronectin. J. Biomed. Sci. 5:173–179 - PubMed
-
- Cheung ST, et al. 1999. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (C666-1) consistently harbouring Epstein-Barr virus. Int. J. Cancer 83:121–126 - PubMed
-
- Colombo E, Alcalay M, Pelicci PG. 2011. Nucleophosmin and its complex network: a possible therapeutic target in hematological diseases. Oncogene 30:2595–2609 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

