Frequent and strong antibody-mediated natural killer cell activation in response to HIV-1 Env in individuals with chronic HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 22496218
- PMCID: PMC3393568
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00569-12
Frequent and strong antibody-mediated natural killer cell activation in response to HIV-1 Env in individuals with chronic HIV-1 infection
Abstract
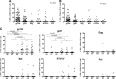
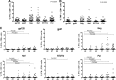
Natural killer (NK) cells play a critical role in the control of HIV-1 infection, and NK cells that respond to HIV-1 peptides have been recently described. However, the mechanisms by which NK cells recognize HIV-1 antigens are not fully understood. We investigated NK cell activation in response to HIV-1 peptides during early and chronic HIV-1 clade B infection using a whole-blood assay and multiparameter flow cytometry. Antibody-mediated NK cell activation in response to HIV-1 peptides was not detected in HIV-1-uninfected individuals. In contrast, 79% of individuals with chronic infection and 22% of individuals with early infection had detectable gamma interferon (IFN-γ) NK cell responses to HIV-1 antigens (P < 0.00001). IFN-γ- and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)-producing NK cells most frequently targeted Env gp120 (median of 4% and range of 0 to 31% of all NK cells). NK cells rarely targeted other HIV-1 proteins such as Gag, Pol, and Nef. Antibody-mediated NK cell responses to peptides mapped predominantly to Env protein, required the presence of plasma or plasma IgG, and resulted in lower CD16 expression on NK cells, suggesting an antibody-mediated activation of NK cells. Further studies are needed to assess the consequences of these antibody-mediated NK cell responses for HIV-1 disease progression and vaccine-induced protection from infection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
NK cell function and antibodies mediating ADCC in HIV-1-infected viremic and controller patients.Viral Immunol. 2011 Oct;24(5):359-68. doi: 10.1089/vim.2011.0025. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Viral Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21958370
-
CD4+ T-cell help enhances NK cell function following therapeutic HIV-1 vaccination.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(15):8349-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00924-14. Epub 2014 May 14. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24829350 Free PMC article.
-
The natural killer cell interferon-gamma response to bacteria is diminished in untreated HIV-1 infection and defects persist despite viral suppression.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2014 Mar 1;65(3):259-67. doi: 10.1097/01.qai.0000435603.50598.2b. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2014. PMID: 24091697 Free PMC article.
-
NK Cells in HIV Disease.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2016 Apr;13(2):85-94. doi: 10.1007/s11904-016-0310-3. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2016. PMID: 27002078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Killer (NK) Cell Education Differentially Influences HIV Antibody-Dependent NK Cell Activation and Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity.Front Immunol. 2017 Aug 24;8:1033. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01033. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28883824 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Different Parameters of Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in HIV Serodiscordant Heterosexual Couples: Humoral Response Potentially Implicated in Modulating Transmission Rates.EBioMedicine. 2017 Dec;26:25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Nov 3. EBioMedicine. 2017. PMID: 29129698 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and Functional Characterization of Circulatory, Splenic, and Hepatic NK Cells in Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Controlling Macaques.J Immunol. 2017 Nov 1;199(9):3202-3211. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700586. Epub 2017 Sep 25. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28947538 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effect of Mucosal NKp44+ Innate Lymphoid Cells and Δγ Cells on Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection Outcome in Rhesus Macaques.J Immunol. 2019 Nov 1;203(9):2459-2471. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900572. Epub 2019 Sep 25. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31554692 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting edge: An antibody recognizing ancestral endogenous virus glycoproteins mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity on HIV-1-infected cells.J Immunol. 2014 Aug 15;193(4):1544-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302108. Epub 2014 Jul 14. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25024383 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR6+ NK Cells in Human Fetal Liver and Spleen Possess Unique Phenotypic and Functional Capabilities.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 19;10:469. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00469. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30941128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alter G, Malenfant JM, Altfeld M. 2004. CD107a as a functional marker for the identification of natural killer cell activity. J. Immunol. Methods 294:15–22 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

