The US16 gene of human cytomegalovirus is required for efficient viral infection of endothelial and epithelial cells
- PMID: 22496217
- PMCID: PMC3393543
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.06310-11
The US16 gene of human cytomegalovirus is required for efficient viral infection of endothelial and epithelial cells
Abstract
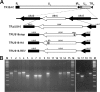
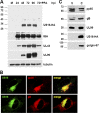
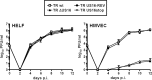
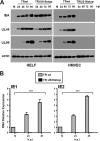
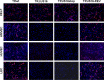
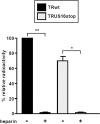
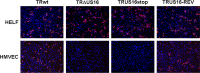
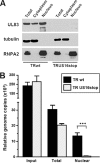
The human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) US12 gene family comprises a set of 10 contiguous genes (US12 to US21), each encoding a predicted seven-transmembrane protein and whose specific functions have yet to be ascertained. While inactivation of individual US12 family members in laboratory strains of HCMV has not been found to affect viral replication in fibroblasts, inactivation of US16 was reported to increase replication in microvascular endothelial cells. Here, we investigate the properties of US16 further by ascertaining the expression pattern of its product. A recombinant HCMV encoding a tagged version of the US16 protein expressed a 33-kDa polypeptide that accumulated with late kinetics in the cytoplasmic virion assembly compartment. To elucidate the function(s) of pUS16, we generated US16-deficient mutants in the TR clinical strain of HCMV. According to previous studies, inactivation of US16 had no effect on viral replication in fibroblasts. In contrast, the US16-deficient viruses exhibited a major growth defect in both microvascular endothelial cells and retinal pigment epithelial cells. The expression of representative IE, E, and L viral proteins was impaired in endothelial cells infected with a US16 mutant virus, suggesting a defect in the replication cycle that occurs prior to IE gene expression. This defect must be due to an inefficient entry and/or postentry event, since pp65 and viral DNA did not move to the nucleus in US16 mutant-infected cells. Taken together, these data indicate that the US16 gene encodes a novel virus tropism factor that regulates, in a cell-specific manner, a pre-immediate-early phase of the HCMV replication cycle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of the Human Cytomegalovirus US16 Protein Abrogates Virus Entry into Endothelial and Epithelial Cells by Reducing the Virion Content of the Pentamer.J Virol. 2017 May 12;91(11):e00205-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00205-17. Print 2017 Jun 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28331097 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of the Human Cytomegalovirus US20 Gene Hampers Productive Viral Replication in Endothelial Cells.J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(21):11092-106. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01141-15. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26311874 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus TR strain glycoprotein O acts as a chaperone promoting gH/gL incorporation into virions but is not present in virions.J Virol. 2010 Mar;84(5):2597-609. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02256-09. Epub 2009 Dec 23. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20032193 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogen at the Gates: Human Cytomegalovirus Entry and Cell Tropism.Viruses. 2018 Dec 11;10(12):704. doi: 10.3390/v10120704. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30544948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus tropism for endothelial/epithelial cells: scientific background and clinical implications.Rev Med Virol. 2010 May;20(3):136-55. doi: 10.1002/rmv.645. Rev Med Virol. 2010. PMID: 20084641 Review.
Cited by
-
High-throughput analysis of human cytomegalovirus genome diversity highlights the widespread occurrence of gene-disrupting mutations and pervasive recombination.J Virol. 2015 Aug 1;89(15):7673-7695. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00578-15. Epub 2015 May 13. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25972543 Free PMC article.
-
Global Mapping of O-Glycosylation of Varicella Zoster Virus, Human Cytomegalovirus, and Epstein-Barr Virus.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 3;291(23):12014-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.721746. Epub 2016 Apr 15. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27129252 Free PMC article.
-
An endothelial cell-specific requirement for the UL133-UL138 locus of human cytomegalovirus for efficient virus maturation.J Virol. 2013 Mar;87(6):3062-75. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02510-12. Epub 2013 Jan 2. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23283945 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Transcriptome of Human Cytomegalovirus: A Comprehensive Review.Viruses. 2023 Aug 8;15(8):1703. doi: 10.3390/v15081703. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37632045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional annotation of human cytomegalovirus gene products: an update.Front Microbiol. 2014 May 19;5:218. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00218. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24904534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adler B, Sinzger C. 2009. Endothelial cells in HCMV infection: one host cell out of many or a crucial target for virus spread? Thromb. Haemost. 102:1057–1063 - PubMed
-
- Bissinger AL, Sinzger C, Kaiserling E, Jahn G. 2002. Human cytomegalovirus as a direct pathogen: correlation of multiorgan involvement and cell distribution with clinical and pathological findings in a case of congenital inclusion disease. J. Med. Virol. 67:200–206 - PubMed
-
- Britt W. 2008. Manifestations of human cytomegalovirus infection: proposed mechanisms of acute and chronic disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 325:417–470 - PubMed
-
- Caposio P, Luganini A, Hahn G, Landolfo S, Gribaudo G. 2007. Activation of the virus-induced IKK/NF-κB signalling axis is critical for the replication of human cytomegalovirus in quiescent cells. Cell. Microbiol. 9:2040–2054 - PubMed

