Extensive terminal and asymmetric processing of small RNAs from rRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, and tRNAs
- PMID: 22492706
- PMCID: PMC3413118
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks307
Extensive terminal and asymmetric processing of small RNAs from rRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, and tRNAs
Abstract
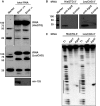
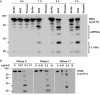
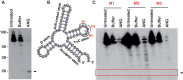
Deep sequencing studies frequently identify small RNA fragments of abundant RNAs. These fragments are thought to represent degradation products of their precursors. Using sequencing, computational analysis, and sensitive northern blot assays, we show that constitutively expressed non-coding RNAs such as tRNAs, snoRNAs, rRNAs and snRNAs preferentially produce small 5' and 3' end fragments. Similar to that of microRNA processing, these terminal fragments are generated in an asymmetric manner that predominantly favors either the 5' or 3' end. Terminal-specific and asymmetric processing of these small RNAs occurs in both mouse and human cells. In addition to the known processing of some 3' terminal tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs) by the RNase III endonuclease Dicer, we show that several RNase family members can produce tRFs, including Angiogenin that cleaves the TψC loop to generate 3' tRFs. The 3' terminal tRFs but not the 5' tRFs are highly complementary to human endogenous retroviral sequences in the genome. Despite their independence from Dicer processing, these tRFs associate with Ago2 and are capable of down regulating target genes by transcript cleavage in vitro. We suggest that endogenous 3' tRFs have a role in regulating the unwarranted expression of endogenous viruses through the RNA interference pathway.
Figures
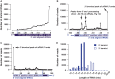
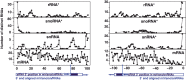
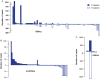
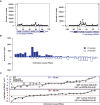

Similar articles
-
Compartmentalized, functional role of angiogenin during spotted fever group rickettsia-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction: evidence of possible mediation by host tRNA-derived small noncoding RNAs.BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Jun 23;13:285. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-285. BMC Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23800282 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast exosome mutants accumulate 3'-extended polyadenylated forms of U4 small nuclear RNA and small nucleolar RNAs.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jan;20(2):441-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.2.441-452.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10611222 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer RNA-derived fragments: origins, processing, and functions.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Nov-Dec;2(6):853-62. doi: 10.1002/wrna.96. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21976287 Review.
-
RIP-seq of BmAgo2-associated small RNAs reveal various types of small non-coding RNAs in the silkworm, Bombyx mori.BMC Genomics. 2013 Sep 28;14:661. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-661. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24074203 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-specific small nucleolar RNAs.J Mol Neurosci. 2006;28(2):103-9. doi: 10.1385/JMN:28:2:103. J Mol Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16679551 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs and tRNA-Derived Small Fragments: Key Messengers in Nuclear-Mitochondrial Communication.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 7;8:643575. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.643575. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34026824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of small RNA sorting into different extracellular fractions revealed by high-throughput sequencing of breast cell lines.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jun 23;43(11):5601-16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv432. Epub 2015 May 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25940616 Free PMC article.
-
Human Argonaute 2 Is Tethered to Ribosomal RNA through MicroRNA Interactions.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 19;291(34):17919-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.725051. Epub 2016 Jun 10. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27288410 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer RNA-Derived Small RNAs: Another Layer of Gene Regulation and Novel Targets for Disease Therapeutics.Mol Ther. 2020 Nov 4;28(11):2340-2357. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.09.013. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32956625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of tRNA-derived fragments in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2023 Feb 13;22(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01739-5. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36782290 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ender C, Krek A, Friedländer MR, Beitzinger M, Weinmann L, Chen W, Pfeffer S, Rajewsky N, Meister G. A human snoRNA with microRNA-like functions. Mol. Cell. 2008;32:519–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

