Activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway in the developing lens stimulates ectopic FoxE3 expression and disruption in fiber cell differentiation
- PMID: 22491411
- PMCID: PMC3385968
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.12-9595
Activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway in the developing lens stimulates ectopic FoxE3 expression and disruption in fiber cell differentiation
Abstract
Purpose: The signaling pathways and transcriptional effectors responsible for directing mammalian lens development provide key regulatory molecules that can inform our understanding of human eye defects. The hedgehog genes encode extracellular signaling proteins responsible for patterning and tissue formation during embryogenesis. Signal transduction of this pathway is mediated through activation of the transmembrane proteins smoothened and patched, stimulating downstream signaling resulting in the activation or repression of hedgehog target genes. Hedgehog signaling is implicated in eye development, and defects in hedgehog signaling components have been shown to result in defects of the retina, iris, and lens.
Methods: We assessed the consequences of constitutive hedgehog signaling in the developing mouse lens using Cre-LoxP technology to express the conditional M2 smoothened allele in the embryonic head and lens ectoderm.
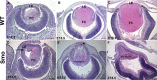
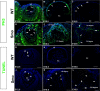
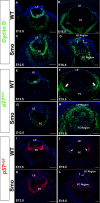
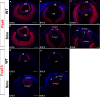
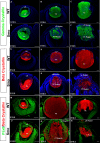
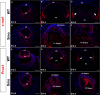
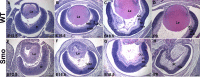
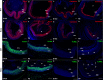
Results: Although initial lens development appeared normal, morphological defects were apparent by E12.5 and became more significant at later stages of embryogenesis. Altered lens morphology correlated with ectopic expression of FoxE3, which encodes a critical gene required for human and mouse lens development. Later, inappropriate expression of the epithelial marker Pax6, and as well as fiber cell markers c-maf and Prox1 also occurred, indicating a failure of appropriate lens fiber cell differentiation accompanied by altered lens cell proliferation and cell death.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that the ectopic activation of downstream effectors of the hedgehog signaling pathway in the mouse lens disrupts normal fiber cell differentiation by a mechanism consistent with a sustained epithelial cellular developmental program driven by FoxE3.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

Similar articles
-
A role for smoothened during murine lens and cornea development.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 30;9(9):e108037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108037. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25268479 Free PMC article.
-
β1-integrin controls cell fate specification in early lens development.Differentiation. 2016 Oct-Nov;92(4):133-147. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2016.08.002. Epub 2016 Sep 3. Differentiation. 2016. PMID: 27596755 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic Pax6 expression disturbs lens fiber cell differentiation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004 Oct;45(10):3589-98. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0151. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004. PMID: 15452066
-
Teleost lens development and degeneration.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2008;269:341-73. doi: 10.1016/S1937-6448(08)01006-X. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18779061 Review.
-
Pathways regulating lens induction in the mouse.Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(8-9):783-91. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.041903rl. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15558471 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of Lens Progenitor Cells and Lentoid Bodies from Pluripotent Stem Cells: Novel Tools for Human Lens Development and Ocular Disease Etiology.Cells. 2022 Nov 6;11(21):3516. doi: 10.3390/cells11213516. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiomics Analysis Reveals Novel Genetic Determinants for Lens Differentiation, Structure, and Transparency.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 19;13(4):693. doi: 10.3390/biom13040693. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in DNA methylation hallmark alterations in chromatin accessibility and gene expression for eye lens differentiation.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2022 Mar 5;15(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13072-022-00440-z. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2022. PMID: 35246225 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of anophthalmia and microphthalmia. Part 2: Syndromes associated with anophthalmia-microphthalmia.Hum Genet. 2019 Sep;138(8-9):831-846. doi: 10.1007/s00439-018-1949-1. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 30374660 Review.
-
A role for smoothened during murine lens and cornea development.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 30;9(9):e108037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108037. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25268479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huangfu D, Anderson KV. Signaling from Smo to Ci/Gli: conservation and divergence of Hedgehog pathways from Drosophila to vertebrates. Development. 2006;133:3–14 - PubMed
-
- Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, et al. Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell. 1996;85:841–851 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

