Enhancers: emerging roles in cell fate specification
- PMID: 22491032
- PMCID: PMC3343362
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2012.52
Enhancers: emerging roles in cell fate specification
Abstract
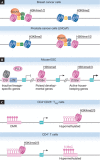
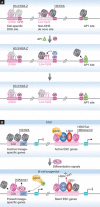
Enhancers are regulatory DNA elements that dictate the spatial and temporal patterns of gene expression during development. Recent evidence suggests that the distinct chromatin features of enhancer regions provide the permissive landscape required for the differential access of diverse signalling molecules that drive cell-specific gene expression programmes. The epigenetic patterning of enhancers occurs before cell fate decisions, suggesting that the epigenetic information required for subsequent differentiation processes is embedded within the enhancer element. Lineage studies indicate that the patterning of enhancers might be regulated by the intricate interplay between DNA methylation status, the binding of specific transcription factors to enhancers and existing histone modifications. In this review, we present insights into the mechanisms of enhancer function, which might ultimately facilitate cell reprogramming strategies for use in regenerative medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
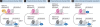


Similar articles
-
Histone ChIP-Seq identifies differential enhancer usage during chondrogenesis as critical for defining cell-type specificity.FASEB J. 2020 Apr;34(4):5317-5331. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902061RR. Epub 2020 Feb 14. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32058623 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of activated enhancers and linked transcription factors in breast, prostate, and kidney tumors by tracing enhancer networks using epigenetic traits.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016 Nov 9;9:50. doi: 10.1186/s13072-016-0102-4. eCollection 2016. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016. PMID: 27833659 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic switch involved in activation of pioneer factor FOXA1-dependent enhancers.Genome Res. 2011 Apr;21(4):555-65. doi: 10.1101/gr.111534.110. Epub 2011 Jan 13. Genome Res. 2011. PMID: 21233399 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin signatures of enhancers and their dynamic regulation.Nucleus. 2023 Dec;14(1):2160551. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2022.2160551. Nucleus. 2023. PMID: 36602897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancer RNA: biogenesis, function, and regulation.Essays Biochem. 2020 Dec 7;64(6):883-894. doi: 10.1042/EBC20200014. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 33034351 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of epigenetics and miRNAs in orofacial clefts.Birth Defects Res. 2020 Nov;112(19):1635-1659. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.1802. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Birth Defects Res. 2020. PMID: 32926553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA transcribed from a distal enhancer is required for activating the chromatin at the promoter of the gonadotropin α-subunit gene.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 7;112(14):4369-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1414841112. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25810254 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting Tissue-Specific Super-Enhancers by Integrating Genome-Wide Analyses and CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2019 Mar;24(1):47-59. doi: 10.1007/s10911-018-9417-z. Epub 2018 Oct 6. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2019. PMID: 30291498 Review.
-
The emerging roles of eRNAs in transcriptional regulatory networks.RNA Biol. 2014;11(2):106-10. doi: 10.4161/rna.27950. Epub 2014 Feb 7. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 24525859 Free PMC article.
-
eQTL mapping in fetal-like pancreatic progenitor cells reveals early developmental insights into diabetes risk.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 30;14(1):6928. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42560-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37903777 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

