Polymer nanoparticle-mediated delivery of microRNA inhibition and alternative splicing
- PMID: 22482958
- PMCID: PMC3366258
- DOI: 10.1021/mp300081s
Polymer nanoparticle-mediated delivery of microRNA inhibition and alternative splicing
Abstract
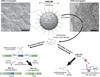
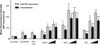
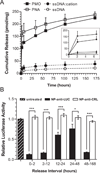
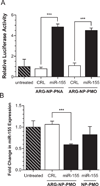
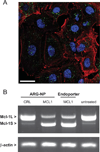
The crux of current RNA-based therapeutics relies on association of synthetic nucleic acids with cellular RNA targets. Antisense oligonucleotide binding to mature microRNA and splicing junctions on pre-mRNA represent methods of gene therapy that respectively inhibit microRNA-mediated gene regulation and induce alternative splicing. We have developed biodegradable polymer nanoparticles, which are coated with cell-penetrating peptides, that can effectively deliver chemically modified oligonucleotide analogues to achieve these forms of gene regulation. We found that this nanoparticle system could block the activity of the oncogenic microRNA, miR-155, as well as modulate splicing to attenuate the expression of the proto-oncogene, Mcl-1. Regulation of these genes in human cancer cells reduced cell viability and produced pro-apoptotic effects. These findings establish polymer nanoparticles as delivery vectors for nonconventional forms of gene therapy activated by cellular delivery of RNA-targeted molecules, which have strong therapeutic implications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
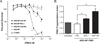
Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle-mediated intratumoral inhibition of miR-21 for improved survival in glioblastoma.Biomaterials. 2019 May;201:87-98. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.02.016. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 30802686 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning Composition of Polymer and Porous Silicon Composite Nanoparticles for Early Endosome Escape of Anti-microRNA Peptide Nucleic Acids.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Sep 2;12(35):39602-39611. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c05827. Epub 2020 Aug 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32805967 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing regulator SLU7 preserves survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and other solid tumors via oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster expression.Oncogene. 2016 Sep 8;35(36):4719-29. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.517. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26804174
-
Advances in Nanoparticle-based Delivery of Next Generation Peptide Nucleic Acids.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(43):5164-5174. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190117164901. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30657037 Review.
-
Enhancing the Effectiveness of Oligonucleotide Therapeutics Using Cell-Penetrating Peptide Conjugation, Chemical Modification, and Carrier-Based Delivery Strategies.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 3;15(4):1130. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041130. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111616 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA delivery for regenerative medicine.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Jul 1;88:108-22. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.05.014. Epub 2015 May 27. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015. PMID: 26024978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogel-mediated delivery of microRNA-92a inhibitor polyplex nanoparticles induces localized angiogenesis.Angiogenesis. 2021 Aug;24(3):657-676. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09778-6. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Angiogenesis. 2021. PMID: 33742265
-
Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Nanoparticle Delivery of Peptide Nucleic Acids In Vivo.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2105:261-281. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0243-0_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32088877 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocarrier mediated delivery of siRNA/miRNA in combination with chemotherapeutic agents for cancer therapy: current progress and advances.J Control Release. 2014 Nov 28;194:238-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Sep 7. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 25204288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology for delivery of peptide nucleic acids (PNAs).J Control Release. 2016 Oct 28;240:302-311. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.01.005. Epub 2016 Jan 8. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26776051 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sebbage V. Cell-penetrating peptides and their therapeutic applications. Biosci. Horiz. 2009;2:64–72.
-
- Astriab-Fisher A, Sergueev D, Fisher M, Shaw BR, Juliano RL. Conjugates of antisense oligonucleotides with the Tat and antennapedia cell-penetrating peptides: effects on cellular uptake, binding to target sequences, and biologic actions. Pharm. Res. 2002;19:744–754. - PubMed
-
- Lennox KA, Behlke MA. Chemical modification and design of anti-miRNA oligonucleotides. Gene Ther. 2011 - PubMed
-
- Moulton HM, Fletcher S, Neuman BW, McClorey G, Stein DA, Abes S, Wilton SD, Buchmeier MJ, Lebleu B, Iversen PL. Cell-penetrating peptide-morpholino conjugates alter pre-mRNA splicing of DMD (Duchenne muscular dystrophy) and inhibit murine coronavirus replication in vivo. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007;35:826–828. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

