Matricellular proteins: a sticky affair with cancers
- PMID: 22481923
- PMCID: PMC3306981
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/351089
Matricellular proteins: a sticky affair with cancers
Abstract
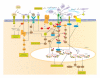
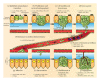
The multistep process of metastasis is a major hallmark of cancer progression involving the cointeraction and coevolution of the tumor and its microenvironment. In the tumor microenvironment, tumor cells and the surrounding stromal cells aberrantly secrete matricellular proteins, which are a family of nonstructural proteins in the extracellular matrix (ECM) that exert regulatory roles via a variety of molecular mechanisms. Matricellular proteins provide signals that support tumorigenic activities characteristic of the metastastic cascade such as epithelial-to-mesenchymal (EMT) transition, angiogenesis, tumor cell motility, proliferation, invasion, evasion from immune surveillance, and survival of anoikis. Herein, we review the current understanding of the following matricellular proteins and highlight their pivotal and multifacted roles in metastatic progression: angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4), CCN family members cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61 (Cyr61/CCN1) and CCN6, osteopontin (OPN), secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC), tenascin C (TNC), and thrombospondin-1 and -2 (TSP1, TSP2). Insights into the signaling mechanisms resulting from the interaction of these matricellular proteins and their respective molecular partner(s), as well as their subsequent contribution to tumor metastasis, are discussed. In addition, emerging evidences of their promising potential as therapeutic options and/or targets in the treatment of cancer are also highlighted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Roles of Matricellular Proteins in Oncogenic Virus-Induced Cancers and Their Potential Utilities as Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Oct 21;18(10):2198. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102198. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29065446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matricellular proteins in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.Adv Cancer Res. 2022;156:249-281. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2022.01.010. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Adv Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35961702 Review.
-
The matricellular protein CCN6 (WISP3) decreases Notch1 and suppresses breast cancer initiating cells.Oncotarget. 2016 May 3;7(18):25180-93. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7734. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26933820 Free PMC article.
-
Embracing the complexity of matricellular proteins: the functional and clinical significance of splice variation.Biomol Concepts. 2016 May 1;7(2):117-32. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2016-0004. Biomol Concepts. 2016. PMID: 27135623 Review.
-
The matricellular protein CYR61 promotes breast cancer lung metastasis by facilitating tumor cell extravasation and suppressing anoikis.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):9200-9215. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13677. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27911269 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of CCN family genes in haematological malignancies.J Cell Commun Signal. 2015 Sep;9(3):267-78. doi: 10.1007/s12079-015-0296-4. Epub 2015 May 31. J Cell Commun Signal. 2015. PMID: 26026820 Free PMC article.
-
Positive and negative influence of the matrix architecture on antitumor immune surveillance.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Dec;70(23):4431-48. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1339-8. Epub 2013 May 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23649148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in 3D Culture Models to Study Exosomes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 22;16(5):883. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050883. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matricellular proteins as regulators of cancer metastasis to bone.Matrix Biol. 2016 May-Jul;52-54:301-314. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Matrix Biol. 2016. PMID: 26807761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of osteopontin silencing on survival and migration of lung cancer cells.Strahlenther Onkol. 2013 Jan;189(1):62-7. doi: 10.1007/s00066-012-0238-5. Epub 2012 Nov 18. Strahlenther Onkol. 2013. PMID: 23161119
References
-
- Chiodoni C, Colombo MP, Sangaletti S. Matricellular proteins: from homeostasis to inflammation, cancer, and metastasis. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews. 2010;29(2):295–307. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

