A combined approach of high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis reveals tissue specific expression of microRNAs and their targets in cucumber
- PMID: 22479356
- PMCID: PMC3316546
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033040
A combined approach of high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis reveals tissue specific expression of microRNAs and their targets in cucumber
Abstract
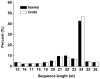
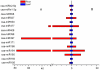
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small RNAs playing an important regulatory function in plant development and stress responses. Among them, some are evolutionally conserved in plant and others are only expressed in certain species, tissue or developmental stages. Cucumber is among the most important greenhouse species in the world, but only a limited number of miRNAs from cucumber have been identified and the experimental validation of the related miRNA targets is still lacking. In this study, two independent small RNA libraries from cucumber leaves and roots were constructed, respectively, and sequenced with the high-throughput Illumina Solexa system. Based on sequence similarity and hairpin structure prediction, a total of 29 known miRNA families and 2 novel miRNA families containing a total of 64 miRNA were identified. QRT-PCR analysis revealed that some of the cucumber miRNAs were preferentially expressed in certain tissues. With the recently developed 'high throughput degradome sequencing' approach, 21 target mRNAs of known miRNAs were identified for the first time in cucumber. These targets were associated with development, reactive oxygen species scavenging, signaling transduction and transcriptional regulation. Our study provides an overview of miRNA expression profile and interaction between miRNA and target, which will help further understanding of the important roles of miRNAs in cucumber plants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Grafting-responsive miRNAs in cucumber and pumpkin seedlings identified by high-throughput sequencing at whole genome level.Physiol Plant. 2014 Aug;151(4):406-22. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12122. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Physiol Plant. 2014. PMID: 24279842
-
MicroRNAs and their targets in cucumber shoot apices in response to temperature and photoperiod.BMC Genomics. 2018 Nov 15;19(1):819. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5204-x. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30442111 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNAs and Their Target Genes Involved in Cucumber Fruit Expansion Using Small RNA and Degradome Sequencing.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 12;9(9):483. doi: 10.3390/biom9090483. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31547414 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA sequencing identifies cucumber miRNA roles in waterlogging-triggered adventitious root primordia formation.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Dec;46(6):6381-6389. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-05084-z. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31538299
-
Drugging the "undruggable" microRNAs.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(5):1861-1871. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03676-8. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33052435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Appropriate Reference Genes for Normalization of miRNA Expression in Grafted Watermelon Plants under Different Nutrient Stresses.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 17;11(10):e0164725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164725. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27749935 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of chilling stress-responsive tomato microRNAs and their target genes by high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis.BMC Genomics. 2014 Dec 17;15(1):1130. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1130. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25519760 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of microRNA targeting impacted by SNPs in cucumber genome.BMC Genomics. 2017 Apr 4;18(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3665-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28376783 Free PMC article.
-
High Throughput Sequencing of Small RNAs in the Two Cucurbita Germplasm with Different Sodium Accumulation Patterns Identifies Novel MicroRNAs Involved in Salt Stress Response.PLoS One. 2015 May 26;10(5):e0127412. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127412. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26010449 Free PMC article.
-
Boron stress responsive microRNAs and their targets in barley.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059543. Epub 2013 Mar 26. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Sunkar R, Chinnusamy V, Zhu JH, Zhu JK. Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci. 2007;12:301–309. - PubMed
-
- Shukla LI, Chinnusamy V, Sunkar R. The role of microRNAs and other endogenous small RNAs in plant stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta-Gene Regul Mech. 2008;1779:743–748. - PubMed
-
- Chuck G, Candela H, Hake S. Big impacts by small RNAs in plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2009;12:81–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

