The lhx2 transcription factor controls thalamocortical axonal guidance by specific regulation of robo1 and robo2 receptors
- PMID: 22457488
- PMCID: PMC6622047
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5851-11.2012
The lhx2 transcription factor controls thalamocortical axonal guidance by specific regulation of robo1 and robo2 receptors
Abstract
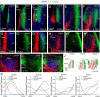
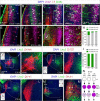
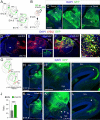
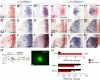
The assembly of neural circuits is dependent upon the generation of specific neuronal subtypes, each subtype displaying unique properties that direct the formation of selective connections with appropriate target cells. Actions of transcription factors in neural progenitors and postmitotic cells are key regulators in this process. LIM-homeodomain transcription factors control crucial aspects of neuronal differentiation, including subtype identity and axon guidance. Nonetheless, their regulation during development is poorly understood and the identity of the downstream molecular effectors of their activity remains largely unknown. Here, we demonstrate that the Lhx2 transcription factor is dynamically regulated in distinct pools of thalamic neurons during the development of thalamocortical connectivity in mice. Indeed, overexpression of Lhx2 provokes defective thalamocortical axon guidance in vivo, while specific conditional deletion of Lhx2 in the thalamus produces topographic defects that alter projections from the medial geniculate nucleus and from the caudal ventrobasal nucleus in particular. Moreover, we demonstrate that Lhx2 influences axon guidance and the topographical sorting of axons by regulating the expression of Robo1 and Robo2 guidance receptors, which are essential for these axons to establish correct connections in the cerebral cortex. Finally, augmenting Robo1 function restores normal axon guidance in Lhx2-overexpressing neurons. By regulating axon guidance receptors, such as Robo1 and Robo2, Lhx2 differentially regulates the axon guidance program of distinct populations of thalamic neurons, thus enabling the establishment of specific neural connections.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gbx2 regulates thalamocortical axon guidance by modifying the LIM and Robo codes.Development. 2012 Dec;139(24):4633-43. doi: 10.1242/dev.086991. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Development. 2012. PMID: 23136391 Free PMC article.
-
Early thalamocortical tract guidance and topographic sorting of thalamic projections requires LIM-homeodomain gene Lhx2.Dev Biol. 2007 Jun 15;306(2):703-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.04.007. Epub 2007 Apr 14. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17493606
-
Spontaneous activity regulates Robo1 transcription to mediate a switch in thalamocortical axon growth.Nat Neurosci. 2012 Jul 8;15(8):1134-43. doi: 10.1038/nn.3160. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22772332
-
Lhx2, an evolutionarily conserved, multifunctional regulator of forebrain development.Brain Res. 2019 Feb 15;1705:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.02.046. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 29522720 Review.
-
Thalamic neuronal specification and early circuit formation.Dev Neurobiol. 2017 Jul;77(7):830-843. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22460. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Dev Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27739248 Review.
Cited by
-
Thalamocortical organoids enable in vitro modeling of 22q11.2 microdeletion associated with neuropsychiatric disorders.Cell Stem Cell. 2024 Mar 7;31(3):421-432.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2024.01.010. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Cell Stem Cell. 2024. PMID: 38382530
-
Lhx2 regulates a cortex-specific mechanism for barrel formation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Dec 10;110(50):E4913-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1311158110. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24262147 Free PMC article.
-
Narrowing the Genetic Causes of Language Dysfunction in the 1q21.1 Microduplication Syndrome.Front Pediatr. 2018 Jun 5;6:163. doi: 10.3389/fped.2018.00163. eCollection 2018. Front Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29922639 Free PMC article.
-
Globularity and language-readiness: generating new predictions by expanding the set of genes of interest.Front Psychol. 2014 Nov 25;5:1324. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01324. eCollection 2014. Front Psychol. 2014. PMID: 25505436 Free PMC article.
-
Robo2 Receptor Gates the Anatomical Divergence of Neurons Derived From a Common Precursor Origin.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 23;9:668175. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.668175. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34249921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews W, Liapi A, Plachez C, Camurri L, Zhang J, Mori S, Murakami F, Parnavelas JG, Sundaresan V, Richards LJ. Robo1 regulates the development of major axon tracts and interneuron migration in the forebrain. Development. 2006;133:2243–2252. - PubMed
-
- Angevine JB., Jr Time of neuron origin in the diencephalon of the mouse. An autoradiographic study. J Comp Neurol. 1970;139:129–187. - PubMed
-
- Bach I. The LIM domain: regulation by association. Mech Dev. 2000;91:5–17. - PubMed
-
- Bagri A, Marín O, Plump AS, Mak J, Pleasure SJ, Rubenstein JL, Tessier-Lavigne M. Slit proteins prevent midline crossing and determine the dorsoventral position of major axonal pathways in the mammalian forebrain. Neuron. 2002;33:233–248. - PubMed
-
- Bielle F, Marcos-Mondéjar P, Leyva-Díaz E, Lokmane L, Mire E, Mailhes C, Keita M, García N, Tessier-Lavigne M, Garel S, López-Bendito G. Emergent growth cone responses to combinations of slit1 and netrin 1 in thalamocortical axon topography. Curr Biol. 2011;21:1748–1755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
