Cellular microRNA let-7c inhibits M1 protein expression of the H1N1 influenza A virus in infected human lung epithelial cells
- PMID: 22452878
- PMCID: PMC3823446
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01572.x
Cellular microRNA let-7c inhibits M1 protein expression of the H1N1 influenza A virus in infected human lung epithelial cells
Abstract
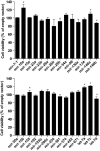
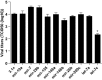
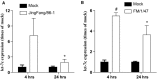
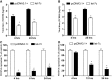
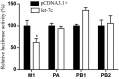
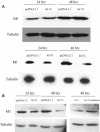
The influenza virus (IV) triggers a series of signalling events inside host cells and induces complex cellular responses. Studies have suggested that host factors play an essential role in IV replication. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) represent a class of small non-coding RNAs that target mRNAs, triggering either translation repression or RNA degradation. Emerging research suggests that host-derived cellular miRNAs are involved in mediating the host-IV interaction. Using miRNA microarrays, we identified several miRNAs aberrantly expressed in IV-infected human lung epithelial cells (A549). Specifically, miR-let-7c was highly up-regulated in IV-infected A549 cells. PITA and miRanda database screening indicated that the let-7c seed sequence is a perfect complementary sequence match to the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of viral gene M1 (+) cRNA, but not to PB2 and PA. As detected by a luciferase reporter system, let-7c directly targeted the 3'-UTR of M1 (+) cRNA, but not PB2 and PA. To experimentally identify the function of cellular let-7c, precursor let-7c was transfected into A549 cells. Let-7c down-regulated IV M1 expression at both the (+) cRNA and protein levels. Furthermore, transfection with a let-7c inhibitor enhanced the expression of M1. Therefore, let-7c may reduce IV replication by degrading M1 (+) cRNA. This is the first report indicating that cellular miRNA regulates IV replication through the degradation of viral gene (+) cRNA by matching the 3'-UTR of the viral cRNA. These findings suggest that let-7c plays a role in protecting host cells from the virus in addition to its known cellular functions.
© 2012 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2012 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cellular microRNAs inhibit replication of the H1N1 influenza A virus in infected cells.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(17):8849-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00456-10. Epub 2010 Jun 16. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20554777 Free PMC article.
-
The highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza A virus down-regulated several cellular MicroRNAs which target viral genome.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Nov;21(11):3076-3086. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13219. Epub 2017 Jun 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28609011 Free PMC article.
-
Host microRNA molecular signatures associated with human H1N1 and H3N2 influenza A viruses reveal an unanticipated antiviral activity for miR-146a.J Gen Virol. 2013 May;94(Pt 5):985-995. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.049528-0. Epub 2013 Jan 23. J Gen Virol. 2013. PMID: 23343627
-
Critical role of microRNAs in host and influenza A (H1N1) virus interactions.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 15;277:119484. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119484. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33862119 Review.
-
Host microRNAs and exosomes that modulate influenza virus infection.Virus Res. 2020 Apr 2;279:197885. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.197885. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 31981772 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of the Interaction between miRNAs and Ebola Virus.Int J Mol Cell Med. 2024;13(2):210-219. doi: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.13.2.210. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2024. PMID: 39184819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human miR-3145 inhibits influenza A viruses replication by targeting and silencing viral PB1 gene.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Dec;240(12):1630-9. doi: 10.1177/1535370215589051. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 26080461 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA hsa-miR-324-5p Suppresses H5N1 Virus Replication by Targeting the Viral PB1 and Host CUEDC2.J Virol. 2018 Sep 12;92(19):e01057-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01057-18. Print 2018 Oct 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30045983 Free PMC article.
-
Host Non-Coding RNA Regulates Influenza A Virus Replication.Viruses. 2021 Dec 29;14(1):51. doi: 10.3390/v14010051. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 35062254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNAs in viral acute respiratory infections: immune regulation, biomarkers, therapy, and vaccines.ExRNA. 2019;1(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s41544-018-0004-7. Epub 2019 Feb 14. ExRNA. 2019. PMID: 34171007 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

