Fragmentation-tree density representation for crystallographic modelling of bound ligands
- PMID: 22446381
- PMCID: PMC3747352
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.03.012
Fragmentation-tree density representation for crystallographic modelling of bound ligands
Abstract
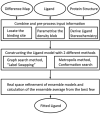
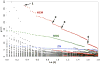
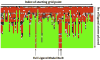
The identification and modelling of ligands into macromolecular models is important for understanding molecule's function and for designing inhibitors to modulate its activities. We describe new algorithms for the automated building of ligands into electron density maps in crystal structure determination. Location of the ligand-binding site is achieved by matching numerical shape features describing the ligand to those of density clusters using a "fragmentation-tree" density representation. The ligand molecule is built using two distinct algorithms exploiting free atoms with inter-atomic connectivity and Metropolis-based optimisation of the conformational state of the ligand, producing an ensemble of structures from which the final model is derived. The method was validated on several thousand entries from the Protein Data Bank. In the majority of cases, the ligand-binding site could be correctly located and the ligand model built with a coordinate accuracy of better than 1 Å. We anticipate that the method will be of routine use to anyone modelling ligands, lead compounds or even compound fragments as part of protein functional analyses or drug design efforts.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
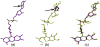

Similar articles
-
Automated identification of crystallographic ligands using sparse-density representations.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Jul;70(Pt 7):1844-53. doi: 10.1107/S1399004714008578. Epub 2014 Jun 29. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014. PMID: 25004962 Free PMC article.
-
Binary image representation of a ligand binding site: its application to efficient sampling of a conformational ensemble.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 May 18;11:256. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-256. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20478076 Free PMC article.
-
Automated ligand placement and refinement with a combined force field and shape potential.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006 Jul;62(Pt 7):741-9. doi: 10.1107/S0907444906016076. Epub 2006 Jun 20. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006. PMID: 16790930
-
Validation of Protein-Ligand Crystal Structure Models: Small Molecule and Peptide Ligands.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1607:611-625. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7000-1_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28573591 Review.
-
Conformational energy range of ligands in protein crystal structures: The difficult quest for accurate understanding.J Mol Recognit. 2017 Aug;30(8):10.1002/jmr.2618. doi: 10.1002/jmr.2618. Epub 2017 Feb 24. J Mol Recognit. 2017. PMID: 28233410 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Visual automated macromolecular model building.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Apr;69(Pt 4):635-41. doi: 10.1107/S0907444913000565. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 23519672 Free PMC article.
-
Automated identification of crystallographic ligands using sparse-density representations.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Jul;70(Pt 7):1844-53. doi: 10.1107/S1399004714008578. Epub 2014 Jun 29. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014. PMID: 25004962 Free PMC article.
-
The quality and validation of structures from structural genomics.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1091:297-314. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-691-7_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24203341 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of the protein-ligand interaction energy for model building and validation.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2017 Mar 1;73(Pt 3):195-202. doi: 10.1107/S2059798317003400. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 28291754 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of HIV-1 replication by integrase-LEDGF allosteric inhibitors is predominant at the post-integration stage.Retrovirology. 2013 Nov 21;10:144. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-144. Retrovirology. 2013. PMID: 24261564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mattos C, Ringe D. Locating and characterizing binding sites on proteins. Nat Biotechnol. 1996;14:595–599. - PubMed
-
- Hartshorn MJ, Murray CW, Cleasby A, Frederickson M, Tickle IJ, Jhoti H. Fragment-based lead discovery using X-ray crystallography. J Med Chem. 2005;48:403–413. - PubMed
-
- Murray CW, Callaghan O, Chessari G, Cleasby A, Congreve M, Frederickson M, et al. Application of fragment screening by X-ray crystallography to β-secretase. J Med Chem. 2007;50:1116–1123. - PubMed
-
- Bosch J, Robien MA, Mehlin C, Boni E, Riechers A, Buckner FS, et al. Using fragment cocktail crystallography to assist inhibitor design of Trypanosoma brucei nucleoside 2-deoxyr-ibosyltransferase. J Med Chem. 2006;49:5939–5946. - PubMed
-
- Wlodek S, Skillman AG, Nicholls A. Automated ligand placement and refinement with a combined force field and shape potential. Acta Crystallogr, Sect D: Biol Crystallogr. 2006;62:741–749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

