Autoregulation of the Drosophila Noncoding roX1 RNA Gene
- PMID: 22438819
- PMCID: PMC3305356
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002564
Autoregulation of the Drosophila Noncoding roX1 RNA Gene
Abstract
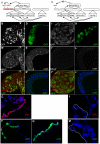
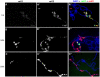
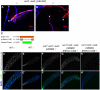
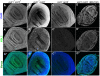
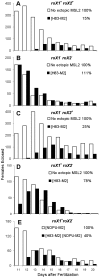
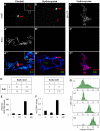
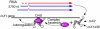
Most genes along the male single X chromosome in Drosophila are hypertranscribed about two-fold relative to each of the two female X chromosomes. This is accomplished by the MSL (male-specific lethal) complex that acetylates histone H4 at lysine 16. The MSL complex contains two large noncoding RNAs, roX1 (RNA on X) and roX2, that help target chromatin modifying enzymes to the X. The roX RNAs are functionally redundant but differ in size, sequence, and transcriptional control. We wanted to find out how roX1 production is regulated. Ectopic DC can be induced in wild-type (roX1(+) roX2(+)) females if we provide a heterologous source of MSL2. However, in the absence of roX2, we found that roX1 expression failed to come on reliably. Using an in situ hybridization probe that is specific only to endogenous roX1, we found that expression was restored if we introduced either roX2 or a truncated but functional version of roX1. This shows that pre-existing roX RNA is required to positively autoregulate roX1 expression. We also observed massive cis spreading of the MSL complex from the site of roX1 transcription at its endogenous location on the X chromosome. We propose that retention of newly assembled MSL complex around the roX gene is needed to drive sustained transcription and that spreading into flanking chromatin contributes to the X chromosome targeting specificity. Finally, we found that the gene encoding the key male-limited protein subunit, msl2, is transcribed predominantly during DNA replication. This suggests that new MSL complex is made as the chromatin template doubles. We offer a model describing how the production of roX1 and msl2, two key components of the MSL complex, are coordinated to meet the dosage compensation demands of the male cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
roX RNAs are required for increased expression of X-linked genes in Drosophila melanogaster males.Genetics. 2006 Dec;174(4):1859-66. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.064568. Epub 2006 Oct 8. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 17028315 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinting of the Y chromosome influences dosage compensation in roX1 roX2 Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2009 Nov;183(3):811-20. doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.107219. Epub 2009 Aug 24. Genetics. 2009. PMID: 19704014 Free PMC article.
-
The roX genes encode redundant male-specific lethal transcripts required for targeting of the MSL complex.EMBO J. 2002 Mar 1;21(5):1084-91. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.5.1084. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11867536 Free PMC article.
-
Path to equality strewn with roX.Dev Biol. 2004 May 1;269(1):18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.01.039. Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15081354 Review.
-
Dosage Compensation of the X Chromosome: A Complex Epigenetic Assignment Involving Chromatin Regulators and Long Noncoding RNAs.Annu Rev Biochem. 2018 Jun 20;87:323-350. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-011816. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Annu Rev Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29668306 Review.
Cited by
-
Factor cooperation for chromosome discrimination in Drosophila.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Feb 28;47(4):1706-1724. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1238. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30541149 Free PMC article.
-
Gene dosage compensation: Origins, criteria to identify compensated genes, and mechanisms including sensor loops as an emerging systems-level property in cancer.Cancer Med. 2023 Dec;12(24):22130-22155. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6719. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37987212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new player in X identification: the CLAMP protein is a key factor in Drosophila dosage compensation.Chromosome Res. 2014 Dec;22(4):505-15. doi: 10.1007/s10577-014-9438-4. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Chromosome Res. 2014. PMID: 25102930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function.Nat Rev Genet. 2016 Jan;17(1):47-62. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2015.10. Nat Rev Genet. 2016. PMID: 26666209 Review.
-
The CLAMP protein links the MSL complex to the X chromosome during Drosophila dosage compensation.Genes Dev. 2013 Jul 15;27(14):1551-6. doi: 10.1101/gad.214585.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23873939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deng X, Meller VH. Non-coding RNA in fly dosage compensation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31:526–532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

