Retinal photodamage mediated by all-trans-retinal
- PMID: 22428905
- PMCID: PMC3424387
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2012.01143.x
Retinal photodamage mediated by all-trans-retinal
Abstract
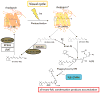
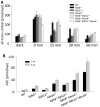
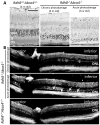
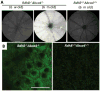
Accumulation of all-trans-retinal (all-trans-RAL), reactive vitamin A aldehyde, is one of the key factors in initiating retinal photodamage. This photodamage is characterized by progressive retinal cell death evoked by light exposure in both an acute and chronic fashion. Photoactivated rhodopsin releases all-trans-RAL, which is subsequently transported by ATP-binding cassette transporter 4 and reduced to all-trans-retinol by all-trans-retinol dehydrogenases located in photoreceptor cells. Any interruptions in the clearing of all-trans-RAL in the photoreceptors can cause an accumulation of this reactive aldehyde and its toxic condensation products. This accumulation may result in the manifestation of retinal dystrophy including human retinal degenerative diseases such as Stargardt's disease and age-related macular degeneration. Herein, we discuss the mechanisms of all-trans-RAL clearance in photoreceptor cells by sequential enzymatic reactions, the visual (retinoid) cycle, and potential molecular pathways of retinal photodamage. We also review recent imaging technologies to monitor retinal health status as well as novel therapeutic strategies preventing all-trans-RAL-associated retinal photodamage.
© 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Photochemistry and Photobiology © 2012 The American Society of Photobiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Limited roles of Rdh8, Rdh12, and Abca4 in all-trans-retinal clearance in mouse retina.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Nov;50(11):5435-43. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-3944. Epub 2009 Jun 24. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19553623 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of all-trans-retinal in acute light-induced retinopathy of mice.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 29;284(22):15173-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900322200. Epub 2009 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19304658 Free PMC article.
-
Light-induced damage to the retina: role of rhodopsin chromophore revisited.Photochem Photobiol. 2005 Nov-Dec;81(6):1305-30. doi: 10.1562/2004-11-13-IR-371. Photochem Photobiol. 2005. PMID: 16120006 Review.
-
Light-induced damage to the retina: current understanding of the mechanisms and unresolved questions: a symposium-in-print.Photochem Photobiol. 2012 Nov-Dec;88(6):1303-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2012.01240.x. Photochem Photobiol. 2012. PMID: 23106541
-
Key enzymes of the retinoid (visual) cycle in vertebrate retina.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1821(1):137-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.03.005. Epub 2011 Apr 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21447403 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid (TUDCA)-Lipid Interactions and Antioxidant Properties of TUDCA Studied in Model of Photoreceptor Membranes.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Apr 29;11(5):327. doi: 10.3390/membranes11050327. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33946822 Free PMC article.
-
Gradual Increase in Environmental Light Intensity Induces Oxidative Stress and Inflammation and Accelerates Retinal Neurodegeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Aug 3;61(10):1. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.10.1. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32744596 Free PMC article.
-
Is There an Optimal Combination of AREDS2 Antioxidants Zeaxanthin, Vitamin E and Vitamin C on Light-Induced Toxicity of Vitamin A Aldehyde to the Retina?Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 9;11(6):1132. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061132. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740030 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenging of Retinoid Cation Radicals by Urate, Trolox, and α-, β-, γ-, and δ-Tocopherols.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 7;20(11):2799. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112799. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31181693 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoid analogs and polyphenols as potential therapeutics for age-related macular degeneration.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 Nov;245(17):1615-1625. doi: 10.1177/1535370220926938. Epub 2020 May 21. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 32438835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McBee JK, Palczewski K, Baehr W, Pepperberg DR. Confronting complexity: the interlink of phototransduction and retinoid metabolism in the vertebrate retina. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001;20:469–529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 EY019031/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY009339/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY011373/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY019880-04/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 EY021126-03/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY019880/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 EY021126-02/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY022658/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY019031-05/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY009339/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY019880/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 EY021126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY 021126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY11373/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY019031-04/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY019031/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY019880-03/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

