IFN-γ-driven IDO production from macrophages protects IL-4Rα-deficient mice against lethality during Schistosoma mansoni infection
- PMID: 22426339
- PMCID: PMC3349826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.01.013
IFN-γ-driven IDO production from macrophages protects IL-4Rα-deficient mice against lethality during Schistosoma mansoni infection
Abstract
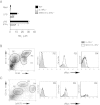
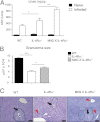
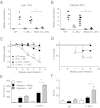
The balance between alternatively activated macrophages (AAMs)/M2 cells and classically activated macrophages (M1 cells) is largely dependent on the effects of IL-4 and interferon (IFN)-γ, respectively. Although AAM/M2 cells can suppress inflammation and repair damaged tissue, M1 cells produce an array of pro-inflammatory molecules. Macrophage effector functions are critical for host protection against many infectious diseases, but it remains unknown whether lethal immunopathological characteristics, caused by Schistosoma mansoni infection in IL-4 receptor α-deficient mice (IL-4Rα(-/-)), results from the absence of M2 cells or increased numbers of M1 cells. In this study, we generated mice that completely lack IL-4Rα signaling in the context of a macrophage-specific loss of IFN-γ responsiveness (MIIG × IL-4Rα(-/-)). Contrary to what we expected, acute schistosomiasis resulted in greater liver injury and mortality in MIIG × IL-4Rα(-/-) mice compared with IL-4Rα(-/-) mice. Greater tissue injury in MIIG × IL-4Rα(-/-) mice was likely because of a lack of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO), a critical regulator of immunosuppression. Indeed, MIIG × IL-4Rα(-/-) failed to up-regulate IDO expression, and IL-4Rα(-/-) mice treated with an IDO antagonist underwent greater liver damage and mortality compared with mock-treated IL-4Rα(-/-) mice. Thus, we propose that, in the absence of AAM/M2 cells, IFN-γ-induced M1 cells suppress tissue-damaging inflammation during acute schistosomiasis through an IDO-dependent mechanism.
Copyright © 2012 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alternative macrophage activation is essential for survival during schistosomiasis and downmodulates T helper 1 responses and immunopathology.Immunity. 2004 May;20(5):623-35. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(04)00107-4. Immunity. 2004. PMID: 15142530
-
IL-4Ralpha-independent expression of mannose receptor and Ym1 by macrophages depends on their IL-10 responsiveness.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010 May 18;4(5):e689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000689. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010. PMID: 20502521 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-4 Receptor Alpha Expressing B Cells Are Essential to Down-Modulate Host Granulomatous Inflammation During Schistosomasis.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 18;9:2928. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02928. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30619289 Free PMC article.
-
Role of IL-4Rα during acute schistosomiasis in mice.Parasite Immunol. 2014 Sep;36(9):421-7. doi: 10.1111/pim.12080. Parasite Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24127774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative activation of macrophages: an immunologic functional perspective.Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:451-83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132532. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19105661 Review.
Cited by
-
Intra-specific variations in Schistosoma mansoni and their possible contribution to inconsistent virulence and diverse clinical outcomes.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Oct 28;18(10):e0012615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012615. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39466851 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Macrophages in the Repair Process during the Tissue Migrating and Resident Helminth Infections.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:8634603. doi: 10.1155/2016/8634603. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27648452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoietic MyD88 and IL-18 are essential for IFN-γ-dependent restriction of type A Francisella tularensis infection.J Leukoc Biol. 2017 Dec;102(6):1441-1450. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4A0517-179R. Epub 2017 Sep 26. J Leukoc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28951422 Free PMC article.
-
Doxycycline hyclate stimulates inducible nitric oxide synthase and arginase imbalance, potentiating inflammatory and oxidative lung damage in schistosomiasis.Biomed J. 2022 Dec;45(6):857-869. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2021.12.007. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Biomed J. 2022. PMID: 34971826 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Dendritic Cells, Regulated by IL-4 Receptor Alpha Signaling, Control Replication, and Dissemination of Leishmania major in Mice.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jan 24;9:479. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00479. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32039054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gryseels B., Polman K., Clerinx J., Kestens L. Human schistosomiasis. Lancet. 2006;368:1106–1118. - PubMed
-
- Brunet L.R., Finkelman F.D., Cheever A.W., Kopf M.A., Pearce E.J. IL-4 protects against TNF-alpha-mediated cachexia and death during acute schistosomiasis. J Immunol. 1997;159:777–785. - PubMed
-
- Nair M.G., Du Y., Perrigoue J.G., Zaph C., Taylor J.J., Goldschmidt M., Swain G.P., Yancopoulos G.D., Valenzuela D.M., Murphy A., Karow M., Stevens S., Pearce E.J., Artis D. Alternatively activated macrophage-derived RELM-{alpha} is a negative regulator of type 2 inflammation in the lung. J Exp Med. 2009;206:937–952. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Phillips S.M., Linette G.P., Doughty B.L., Byram J.E., Von Lichtenberg F. In vivo T cell depletion regulates resistance and morbidity in murine schistosomiasis. J Immunol. 1987;139:919–926. - PubMed
-
- Fallon P.G., Richardson E.J., McKenzie G.J., McKenzie A.N. Schistosome infection of transgenic mice defines distinct and contrasting pathogenic roles for IL-4 and IL-13: IL-13 is a profibrotic agent. J Immunol. 2000;164:2585–2591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

