CNVs: harbingers of a rare variant revolution in psychiatric genetics
- PMID: 22424231
- PMCID: PMC3351385
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.039
CNVs: harbingers of a rare variant revolution in psychiatric genetics
Abstract
The genetic bases of neuropsychiatric disorders are beginning to yield to scientific inquiry. Genome-wide studies of copy number variation (CNV) have given rise to a new understanding of disease etiology, bringing rare variants to the forefront. A proportion of risk for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and autism can be explained by rare mutations. Such alleles arise by de novo mutation in the individual or in recent ancestry. Alleles can have specific effects on behavioral and neuroanatomical traits; however, expressivity is variable, particularly for neuropsychiatric phenotypes. Knowledge from CNV studies reflects the nature of rare alleles in general and will serve as a guide as we move forward into a new era of whole-genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

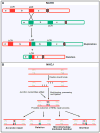

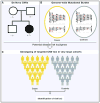
Similar articles
-
New technologies provide insights into genetic basis of psychiatric disorders and explain their co-morbidity.Psychiatr Danub. 2010 Jun;22(2):190-2. Psychiatr Danub. 2010. PMID: 20562745 Review.
-
Comprehensive cross-disorder analyses of CNTNAP2 suggest it is unlikely to be a primary risk gene for psychiatric disorders.PLoS Genet. 2018 Dec 26;14(12):e1007535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007535. eCollection 2018 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30586385 Free PMC article.
-
Rare copy number variants: a point of rarity in genetic risk for bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010 Apr;67(4):318-27. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.25. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20368508 Free PMC article.
-
High frequencies of de novo CNVs in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.Neuron. 2011 Dec 22;72(6):951-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.007. Neuron. 2011. PMID: 22196331 Free PMC article.
-
Autism genetics: emerging data from genome-wide copy-number and single nucleotide polymorphism scans.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009 Nov;9(8):795-803. doi: 10.1586/erm.09.59. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009. PMID: 19895225 Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges in understanding psychiatric disorders and developing therapeutics: a role for zebrafish.Dis Model Mech. 2015 Jul 1;8(7):647-56. doi: 10.1242/dmm.019620. Dis Model Mech. 2015. PMID: 26092527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Heterogeneity Shapes Brain Connectivity in Psychiatry.Biol Psychiatry. 2023 Jan 1;93(1):45-58. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2022.08.024. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Biol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36372570 Free PMC article.
-
Autism genetics: searching for specificity and convergence.Genome Biol. 2012 Jul 31;13(7):247. doi: 10.1186/gb4034. Genome Biol. 2012. PMID: 22849751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain functional connectivity mirrors genetic pleiotropy in psychiatric conditions.Brain. 2023 Apr 19;146(4):1686-1696. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac315. Brain. 2023. PMID: 36059063 Free PMC article.
-
Is Poor Working Memory a Transdiagnostic Risk Factor for Psychopathology?J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017 Nov;45(8):1477-1490. doi: 10.1007/s10802-016-0219-8. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017. PMID: 27783257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkuraya FS. Homozygosity mapping: one more tool in the clinical geneticist’s toolbox. Genet Med. 2010;12:236–239. - PubMed
-
- Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, Bolton P, Simonoff E, Yuzda E, Rutter M. Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med. 1995;25:63–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

