Liver T1ρ MRI measurement in healthy human subjects at 3 T: a preliminary study with a two-dimensional fast-field echo sequence
- PMID: 22422392
- PMCID: PMC3487072
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/98745548
Liver T1ρ MRI measurement in healthy human subjects at 3 T: a preliminary study with a two-dimensional fast-field echo sequence
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to explore the technical feasibility of T(1)ρ MRI for the liver, and to determine the normal range of liver T(1)ρ in healthy subjects at clinical 3 T.
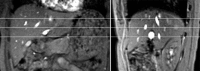
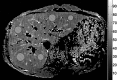
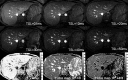
Methods: There were 15 healthy volunteers. Three representative axial slices were selected to cut through the upper, middle and lower liver. A rotary echo spin-lock pulse was implemented in a two-dimensional fast-field echo sequence. Spin-lock frequency was 500 Hz, and the spin-lock times of 1, 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 ms were used for T(1)ρ mapping. The images were acquired slice by slice during breath-holding. Regions of interest (ROIs; n=5) were manually placed on each slice of the liver parenchyma region, excluding artefacts and vessels. The mean value of these ROIs (n=15) was regarded as the liver T(1)ρ value for the subject. Six subjects were scanned once at fasting status; six subjects were scanned once 2 h post meal; three subjects were scanned twice at fasting status; and seven subjects were scanned twice 2 h post meal.
Results: When two readers measured the same 10 data sets, the interreader reproducibility (ICC: intraclass correlation coefficient) was 0.955. With the 10 subjects scanned twice, the ICC for scan-rescan reproducibility was 0.764. There was no significant difference for the liver T(1)ρ value at the fasting status (43.08±1.41 ms) and post-meal status (42.97±2.38 ms, p=0.867). Pooling together all the 32 scans in this study, the normal liver T(1)ρ value ranged from 38.6 to 48.3 ms (mean 43.0 ms, median 42.6 ms).
Conclusion: It is feasible to obtain consistent liver T(1)ρ measurement for human subjects at 3 T.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experimental evaluation of accelerated T1rho relaxation quantification in human liver using limited spin-lock times.Korean J Radiol. 2012 Nov-Dec;13(6):736-42. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.736. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Korean J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 23118572 Free PMC article.
-
Further exploration of MRI techniques for liver T1rho quantification.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2013 Dec;3(6):308-15. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2013.12.10. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2013. PMID: 24404445 Free PMC article.
-
Breath-hold black-blood T1rho mapping improves liver T1rho quantification in healthy volunteers.Acta Radiol. 2018 Mar;59(3):257-265. doi: 10.1177/0284185117717764. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Acta Radiol. 2018. PMID: 28679324
-
Comparison of multislice breath-hold and 3D respiratory triggered T1 ρ imaging of liver in healthy volunteers and liver cirrhosis patients in 3.0 T MRI.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Oct;44(4):906-13. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25253. Epub 2016 May 5. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27149283
-
Liver imaging at 3.0 T: diffusion-induced black-blood echo-planar imaging with large anatomic volumetric coverage as an alternative for specific absorption rate-intensive echo-train spin-echo sequences: feasibility study.Radiology. 2008 Jul;248(1):264-71. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2481070034. Radiology. 2008. PMID: 18566178
Cited by
-
Development of a novel rat model of heterogeneous hepatic injury by injection with colchicine via the splenic vein.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov 28;24(44):5005-5012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i44.5005. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30510375 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of liver fibrosis with T1ρ MR imaging.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2014 Jun;4(3):152-5. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2014.04.04. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2014. PMID: 24914415 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Impact of Liver Fibrosis and Fatty Liver on T1rho Measurements: A Prospective Study.Korean J Radiol. 2017 Nov-Dec;18(6):898-905. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2017.18.6.898. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Korean J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 29089822 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of Hepatic Fibrosis.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2018 Aug 29;20(10):45. doi: 10.1007/s11894-018-0652-7. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30159792 Review.
-
T1ρ MRI of healthy and fibrotic human livers at 1.5 T.J Transl Med. 2015 Sep 8;13:292. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0648-0. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26350896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davis GL, Albright JE, Cook SF, Rosenberg DM. Projecting future complications of chronic hepatitis C in the United States. Liver Transpl 2003;9:331–8 - PubMed
-
- Charlton M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review of current understanding and future impact. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;2:1048–58 - PubMed
-
- Wallace K, Burt AD, Wright MC. Liver fibrosis. Biochem J 2008;411:1–18 - PubMed
-
- Leung NW, Lai CL, Chang TT, Guan R, Lee CM, Ng KY, et al. Extended lamivudine treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B enhances hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion rates: results after 3 years of therapy. Hepatology 2001;33:1527–32 - PubMed
-
- Hammel P, Couvelard A, O'Toole D, Ratouis A, Sauvanet A, Flejou JF, et al. Regression of liver fibrosis after biliary drainage in patients with chronic pancreatitis and stenosis of the common bile duct. N Engl J Med 2001;344:418–23 - PubMed

