Caveolins and lung function
- PMID: 22411320
- PMCID: PMC3449096
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4614-1222-9_11
Caveolins and lung function
Abstract
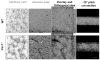
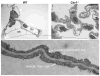
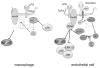
The primary function of the mammalian lung is to facilitate diffusion of oxygen to venous blood and to ventilate carbon dioxide produced by catabolic reactions within cells. However, it is also responsible for a variety of other important functions, including host defense and production of vasoactive agents to regulate not only systemic blood pressure, but also water, electrolyte and acid-base balance. Caveolin-1 is highly expressed in the majority of cell types in the lung, including epithelial, endothelial, smooth muscle, connective tissue cells, and alveolar macrophages. Deletion of caveolin-1 in these cells results in major functional aberrations, suggesting that caveolin-1 may be crucial to lung homeostasis and development. Furthermore, generation of mutant mice that under-express caveolin-1 results in severe functional distortion with phenotypes covering practically the entire spectrum of known lung diseases, including pulmonary hypertension, fibrosis, increased endothelial permeability, and immune defects. In this Chapter, we outline the current state of knowledge regarding caveolin-1-dependent regulation of pulmonary cell functions and discuss recent research findings on the role of caveolin-1 in various pulmonary disease states, including obstructive and fibrotic pulmonary vascular and inflammatory diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loss of caveolae, vascular dysfunction, and pulmonary defects in caveolin-1 gene-disrupted mice.Science. 2001 Sep 28;293(5539):2449-52. doi: 10.1126/science.1062688. Epub 2001 Aug 9. Science. 2001. PMID: 11498544
-
The Caveolin genes: from cell biology to medicine.Ann Med. 2004;36(8):584-95. doi: 10.1080/07853890410018899. Ann Med. 2004. PMID: 15768830 Review.
-
The alpha-isoform of caveolin-1 is a marker of vasculogenesis in early lung development.J Histochem Cytochem. 2002 Jan;50(1):33-42. doi: 10.1177/002215540205000104. J Histochem Cytochem. 2002. PMID: 11748292
-
Caveolin-2-deficient mice show evidence of severe pulmonary dysfunction without disruption of caveolae.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;22(7):2329-44. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2329-2344.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11884617 Free PMC article.
-
Functional morphology of the distal lung.Int Rev Cytol. 1974;37(0):153-270. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61359-5. Int Rev Cytol. 1974. PMID: 4599700 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Aging Human Lung Mucosa: A Proteomics Study.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022 Oct 6;77(10):1969-1974. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glac091. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35460553 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the loss of caveolin-1 on lung mass and cholesterol metabolism in mice with and without the lysosomal cholesterol transporter, Niemann-Pick type C1.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jul;1841(7):995-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24747682 Free PMC article.
-
Tagging strategies strongly affect the fate of overexpressed caveolin-1.Traffic. 2015 Apr;16(4):417-38. doi: 10.1111/tra.12254. Traffic. 2015. PMID: 25639341 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial glutathione: features, regulation and role in disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 May;1830(5):3317-28. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.10.018. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23123815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Caveolin-1 in Sepsis - A Mini-Review.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 15;13:902907. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.902907. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- West JB, Watson RR, Fu Z. The human lung: did evolution get it wrong? Eur Respir J. 2007;29(1):11–17. - PubMed
-
- West JB. Thoughts on the pulmonary blood-gas barrier. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;285(3):L501–L513. - PubMed
-
- Gehr P, Bachofen M, Weibel ER. The normal human lung: ultrastructure and morphometric estimation of diffusion capacity. Respir Physiol. 1978;32(2):121–140. - PubMed
-
- Phillips CG, Kaye SR. On the asymmetry of bifurcations in the bronchial tree. Respir Physiol. 1997;107(1):85–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

