Yeast mitochondrial interactosome model: metabolon membrane proteins complex involved in the channeling of ADP/ATP
- PMID: 22408429
- PMCID: PMC3291998
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms13021858
Yeast mitochondrial interactosome model: metabolon membrane proteins complex involved in the channeling of ADP/ATP
Abstract
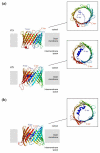
The existence of a mitochondrial interactosome (MI) has been currently well established in mammalian cells but the exact composition of this super-complex is not precisely known, and its organization seems to be different from that in yeast. One major difference is the absence of mitochondrial creatine kinase (MtCK) in yeast, unlike that described in the organization model of MI, especially in cardiac, skeletal muscle and brain cells. The aim of this review is to provide a detailed description of different partner proteins involved in the synergistic ADP/ATP transport across the mitochondrial membranes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and to propose a new mitochondrial interactosome model. The ADP/ATP (Aacp) and inorganic phosphate (PiC) carriers as well as the VDAC (or mitochondrial porin) catalyze the import and export of ADP, ATP and Pi across the mitochondrial membranes. Aacp and PiC, which appear to be associated with the ATP synthase, consist of two nanomotors (F(0), F(1)) under specific conditions and form ATP synthasome. Identification and characterization of such a complex were described for the first time by Pedersen and co-workers in 2003.
Keywords: ADP/ATP carrier; ATP synthasome; VDAC; diffusion; inorganic phosphate carrier; metabolic microcompartmentation; metabolon; mitochondrial interactosome; phosphotransfer network.
Figures
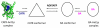

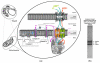
Similar articles
-
Transport of adenine nucleotides in the mitochondria of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: interactions between the ADP/ATP carriers and the ATP-Mg/Pi carrier.Mitochondrion. 2009 Apr;9(2):79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2009.01.001. Epub 2009 Jan 17. Mitochondrion. 2009. PMID: 19460304 Review.
-
The transport mechanism of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Oct;1863(10):2379-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.03.015. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27001633 Review.
-
Membrane potential stimulates ADP import and ATP export by the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier due to its positively charged binding site.Sci Adv. 2024 Nov;10(44):eadp7725. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp7725. Epub 2024 Nov 1. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39485853 Free PMC article.
-
High efficiency of energy flux controls within mitochondrial interactosome in cardiac intracellular energetic units.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Dec;1807(12):1549-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21872567
-
Conformation-dependent swinging of the matrix loop m2 of the mitochondrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae ADP/ATP carrier.Biochemistry. 2005 Dec 13;44(49):16310-20. doi: 10.1021/bi0514820. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 16331992
Cited by
-
Inhibition of the mitochondrial ATPase function by IF1 changes the spatiotemporal organization of ATP synthase.Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2021 Jan 1;1862(1):148322. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2020.148322. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2021. PMID: 33065099 Free PMC article.
-
Elements of the cellular metabolic structure.Front Mol Biosci. 2015 Apr 28;2:16. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2015.00016. eCollection 2015. Front Mol Biosci. 2015. PMID: 25988183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clémençon B., Rey M., Dianoux A.C., Trézéguet V., Lauquin G.J., Brandolin G., Pelosi L. Structure-function relationships of the C-terminal end of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ADP/ATP carrier isoform 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:11218–11225. - PubMed
-
- Verkman A.S. Solute and macromolecule diffusion in cellular aqueous compartments. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002;27:27–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

