Charting the NF-κB pathway interactome map
- PMID: 22403694
- PMCID: PMC3293857
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032678
Charting the NF-κB pathway interactome map
Abstract
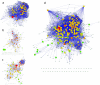
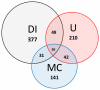
Inflammation is part of a complex physiological response to harmful stimuli and pathogenic stress. The five components of the Nuclear Factor κB (NF-κB) family are prominent mediators of inflammation, acting as key transcriptional regulators of hundreds of genes. Several signaling pathways activated by diverse stimuli converge on NF-κB activation, resulting in a regulatory system characterized by high complexity. It is increasingly recognized that the number of components that impinges upon phenotypic outcomes of signal transduction pathways may be higher than those taken into consideration from canonical pathway representations. Scope of the present analysis is to provide a wider, systemic picture of the NF-κB signaling system. Data from different sources such as literature, functional enrichment web resources, protein-protein interaction and pathway databases have been gathered, curated, integrated and analyzed in order to reconstruct a single, comprehensive picture of the proteins that interact with, and participate to the NF-κB activation system. Such a reconstruction shows that the NF-κB interactome is substantially different in quantity and quality of components with respect to canonical representations. The analysis highlights that several neglected but topologically central proteins may play a role in the activation of NF-κB mediated responses. Moreover the interactome structure fits with the characteristics of a bow tie architecture. This interactome is intended as an open network resource available for further development, refinement and analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Possible role of NF-κB in hormesis during ageing.Biogerontology. 2012 Dec;13(6):637-46. doi: 10.1007/s10522-012-9402-7. Biogerontology. 2012. PMID: 23053821
-
TNIP2 is a Hub Protein in the NF-κB Network with Both Protein and RNA Mediated Interactions.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Nov;15(11):3435-3449. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.060509. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27609421 Free PMC article.
-
14-3-3 epsilon dynamically interacts with key components of mitogen-activated protein kinase signal module for selective modulation of the TNF-alpha-induced time course-dependent NF-kappaB activity.J Proteome Res. 2010 Jul 2;9(7):3465-78. doi: 10.1021/pr9011377. J Proteome Res. 2010. PMID: 20462248
-
Non-canonical NF-κB signaling activation and regulation: principles and perspectives.Immunol Rev. 2011 Nov;244(1):44-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01059.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22017430 Review.
-
The NF-kappaB regulatory network.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2006;6(2):111-30. doi: 10.1385/ct:6:2:111. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 17303919 Review.
Cited by
-
Loki zupa alleviates inflammatory and fibrotic responses in cigarette smoke induced rat model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Chin Med. 2020 Aug 31;15:92. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-00373-3. eCollection 2020. Chin Med. 2020. PMID: 32874197 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic Signaling Induced by HCV Infection.Viruses. 2018 Oct 2;10(10):538. doi: 10.3390/v10100538. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30279347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On chaotic dynamics in transcription factors and the associated effects in differential gene regulation.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 8;10(1):71. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07932-1. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30622249 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes and metabolic syndrome as risk factors for COVID-19.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020 Jul-Aug;14(4):671-677. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.05.013. Epub 2020 May 8. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020. PMID: 32438331 Free PMC article.
-
Systems biology for molecular life sciences and its impact in biomedicine.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Mar;70(6):1035-53. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1109-z. Epub 2012 Aug 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22903296 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- De Martinis M, Franceschi C, Monti D, Ginaldi L. Inflamm-ageing and lifelong antigenic load as major determinants of ageing rate and longevity. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:2035–2039. - PubMed
-
- Fagiolo U, Cossarizza A, Scala E, Fanales-Belasio E, Ortolani C, et al. Increased cytokine production in mononuclear cells of healthy elderly people. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23:2375–2378. - PubMed
-
- Alberti S, Cevenini E, Ostan R, Capri M, Salvioli S, et al. Age-dependent modifications of Type 1 and Type 2 cytokines within virgin and memory CD4+ T cells in humans. Mech Ageing Dev. 2006;127:560–566. - PubMed
-
- Wikby A, Nilsson BO, Forsey R, Thompson J, Strindhall J, et al. The immune risk phenotype is associated with IL-6 in the terminal decline stage: findings from the Swedish NONA immune longitudinal study of very late life functioning. Mech Ageing Dev. 2006;127:695–704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

