NEU1 and NEU3 sialidase activity expressed in human lung microvascular endothelia: NEU1 restrains endothelial cell migration, whereas NEU3 does not
- PMID: 22403397
- PMCID: PMC3346112
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.346817
NEU1 and NEU3 sialidase activity expressed in human lung microvascular endothelia: NEU1 restrains endothelial cell migration, whereas NEU3 does not
Abstract
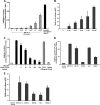
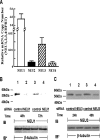
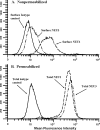
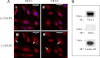
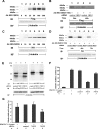
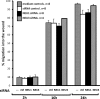
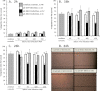
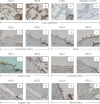
The microvascular endothelial surface expresses multiple molecules whose sialylation state regulates multiple aspects of endothelial function. To better regulate these sialoproteins, we asked whether endothelial cells (ECs) might express one or more catalytically active sialidases. Human lung microvascular EC lysates contained heat-labile sialidase activity for a fluorogenic substrate, 2'-(4-methylumbelliferyl)-α-D-N-acetylneuraminic acid (4-MU-NANA), that was dose-dependently inhibited by the competitive sialidase inhibitor, 2,3-dehydro-2-deoxy-N-acetylneuraminic acid but not its negative control. The EC lysates also contained sialidase activity for a ganglioside mixture. Using real time RT-PCR to detect mRNAs for the four known mammalian sialidases, NEU1, -2, -3, and -4, NEU1 mRNA was expressed at levels 2700-fold higher that those found for NEU2, -3, or -4. Western analyses indicated NEU1 and -3 protein expression. Using confocal microscopy and flow cytometry, NEU1 was immunolocalized to both the plasma membrane and the perinuclear region. NEU3 was detected both in the cytosol and nucleus. Prior siRNA-mediated knockdown of NEU1 and NEU3 each decreased EC sialidase activity for 4-MU-NANA by >65 and >17%, respectively, and for the ganglioside mixture by 0 and 40%, respectively. NEU1 overexpression in ECs reduced their migration into a wound by >40%, whereas NEU3 overexpression did not. Immunohistochemical studies of normal human tissues immunolocalized NEU1 and NEU3 proteins to both pulmonary and extrapulmonary vascular endothelia. These combined data indicate that human lung microvascular ECs as well as other endothelia express catalytically active NEU1 and NEU3. NEU1 restrains EC migration, whereas NEU3 does not.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NEU1 sialidase regulates the sialylation state of CD31 and disrupts CD31-driven capillary-like tube formation in human lung microvascular endothelia.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 28;289(13):9121-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.555888. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24550400 Free PMC article.
-
The NEU1-selective sialidase inhibitor, C9-butyl-amide-DANA, blocks sialidase activity and NEU1-mediated bioactivities in human lung in vitro and murine lung in vivo.Glycobiology. 2016 Aug;26(8):834-49. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cww060. Epub 2016 May 25. Glycobiology. 2016. PMID: 27226251 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of endogenous sialidases of human monocytes during cellular differentiation into macrophages.FEBS J. 2005 May;272(10):2545-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04679.x. FEBS J. 2005. PMID: 15885103
-
Sialidase NEU3 and its pathological significance.Glycoconj J. 2022 Oct;39(5):677-683. doi: 10.1007/s10719-022-10067-7. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Glycoconj J. 2022. PMID: 35675020 Review.
-
Cellular translocation and secretion of sialidases.J Biol Chem. 2024 Sep;300(9):107671. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107671. Epub 2024 Aug 14. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39128726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Galectin-1 mediates interactions between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and vascular endothelial cells, and promotes their extravasation during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury.Mol Immunol. 2023 Apr;156:127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2023.02.011. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36921487 Free PMC article.
-
NEU1 sialidase regulates the sialylation state of CD31 and disrupts CD31-driven capillary-like tube formation in human lung microvascular endothelia.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 28;289(13):9121-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.555888. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24550400 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting protein glycosylation to regulate inflammation in the respiratory tract: novel diagnostic and therapeutic candidates for chronic respiratory diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 May 15;14:1168023. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1168023. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37256139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Effect of Neuraminidase-1-Selective Inhibition in Mouse Models of Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021 Jan;376(1):136-146. doi: 10.1124/jpet.120.000223. Epub 2020 Nov 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021. PMID: 33139318 Free PMC article.
-
Altered IgG glycosylation at COVID-19 diagnosis predicts disease severity.Eur J Immunol. 2022 Jun;52(6):946-957. doi: 10.1002/eji.202149491. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Eur J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35307819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith C. W. (2008) Adhesion molecules and receptors. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 121, S375–S379 - PubMed
-
- Stevens T., Garcia J. G., Shasby D. M., Bhattacharya J., Malik A. B. (2000) Mechanisms regulating endothelial cell barrier function. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 279, L419–L422 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

