Pax6 is crucial for β-cell function, insulin biosynthesis, and glucose-induced insulin secretion
- PMID: 22403172
- PMCID: PMC5417143
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2011-1256
Pax6 is crucial for β-cell function, insulin biosynthesis, and glucose-induced insulin secretion
Abstract
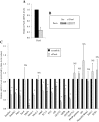
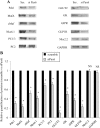
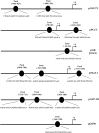
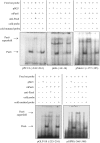
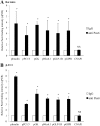
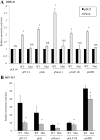
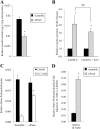
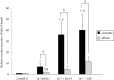
The Pax6 transcription factor is crucial for endocrine cell differentiation and function. Indeed, mutations of Pax6 are associated with a diabetic phenotype and a drastic decrease of insulin-positive cell number. Our aim was to better define the β-cell Pax6 transcriptional network and thus provide further information concerning the role of Pax6 in β-cell function. We developed a Pax6-deficient model in rat primary β-cells with specific small interfering RNA leading to a 75% knockdown of Pax6 expression. Through candidate gene approach, we confirmed that Pax6 controls the mRNA levels of the insulin 1 and 2, Pdx1, MafA, GLUT2, and PC1/3 genes in β-cells. Importantly, we identified new Pax6 target genes coding for GK, Nkx6.1, cMaf, PC2, GLP-1R and GIPR which are all involved in β-cell function. Furthermore, we demonstrated that Pax6 directly binds and activates specific elements on the promoter region of these genes. We also demonstrated that Pax6 knockdown led to decreases in insulin cell content, in insulin processing, and a specific defect of glucose-induced insulin secretion as well as a significant reduction of GLP-1 action in primary β-cells. Our results strongly suggest that Pax6 is crucial for β-cells through transcriptional control of key genes coding for proteins that are involved in insulin biosynthesis and secretion as well as glucose and incretin actions on β-cells. We provide further evidence that Pax6 represents a key element of mature β-cell function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pax6 is a key component of regulated glucagon secretion.Endocrinology. 2012 Sep;153(9):4204-15. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1425. Epub 2012 Jul 9. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22778220
-
Pax6 controls the expression of critical genes involved in pancreatic {alpha} cell differentiation and function.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 22;285(43):33381-33393. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.147215. Epub 2010 Jun 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20592023 Free PMC article.
-
The activation of the rat insulin gene II by BETA2 and PDX-1 in rat insulinoma cells is repressed by Pax6.Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Dec;24(12):2331-42. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0220. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Mol Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20943817 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic Beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013 Jan 1;9(1):25-53. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013. PMID: 22974359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucagon gene expression in the endocrine pancreas: the role of the transcription factor Pax6 in α-cell differentiation, glucagon biosynthesis and secretion.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011 Oct;13 Suppl 1:31-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2011.01445.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011. PMID: 21824254 Review.
Cited by
-
TAZ promotes PDX1-mediated insulinogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Mar 13;79(3):186. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04216-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35279781 Free PMC article.
-
Homocysteine Metabolism Pathway Is Involved in the Control of Glucose Homeostasis: A Cystathionine Beta Synthase Deficiency Study in Mouse.Cells. 2022 May 25;11(11):1737. doi: 10.3390/cells11111737. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681432 Free PMC article.
-
Microphthalmia transcription factor regulates pancreatic β-cell function.Diabetes. 2013 Aug;62(8):2834-42. doi: 10.2337/db12-1464. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23610061 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating single cell transcriptomics and volume electron microscopy confirms the presence of pancreatic acinar-like cells in sea urchins.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 19;10:991664. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.991664. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36060803 Free PMC article.
-
PDX1 Methylation, NGN3 and Pax6 Expression Levels in Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and their association with neonatal blood sugars and birth weight.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Jan-Feb;40(3Part-II):509-513. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.3.7700. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38356808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walther C , Gruss P. 1991. Pax-6, a murine paired box gene, is expressed in the developing CNS. Development 113:1435–1449 - PubMed
-
- Turque N , Plaza S , Radvanyi F , Carriere C , Saule S. 1994. Pax-QNR/Pax-6, a paired box- and homeobox-containing gene expressed in neurons, is also expressed in pancreatic endocrine cells. Mol Endocrinol 8:929–938 - PubMed
-
- St-Onge L , Sosa-Pineda B , Chowdhury K , Mansouri A , Gruss P. 1997. Pax6 is required for differentiation of glucagon-producing α-cells in mouse pancreas. Nature 387:406–409 - PubMed
-
- Sander M , Neubüser A , Kalamaras J , Ee HC , Martin GR , German MS. 1997. Genetic analysis reveals that PAX6 is required for normal transcription of pancreatic hormone genes and islet development. Genes Dev 11:1662–1673 - PubMed
-
- Ashery-Padan R , Zhou X , Marquardt T , Herrera P , Toube L , Berry A , Gruss P. 2004. Conditional inactivation of Pax6 in the pancreas causes early onset of diabetes. Dev Biol 269:479–488 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

