Diet-induced weight loss in overweight or obese women and changes in high-density lipoprotein levels and function
- PMID: 22402736
- PMCID: PMC3374067
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2012.56
Diet-induced weight loss in overweight or obese women and changes in high-density lipoprotein levels and function
Abstract
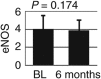
Diet-induced weight loss in women may be associated with decreases not only in plasma levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), but also in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Whether a decrease in HDL-C is associated with altered HDL function is unknown. One hundred overweight or obese women (age 46 ± 11 years, 60 black; 12 diabetic) were enrolled in the 6-month program of reduced fat and total energy diet and low-intensity exercise. Serum cholesterol efflux capacity was measured in (3)H-cholesterol-labeled BHK cells expressing ABCA1, ABCG1, or SR-B1 transporters and incubated with 1% apolipoprotein B (apoB)-depleted serum. Antioxidant properties of HDL were estimated by paraoxonase-1 (PON1) activity and oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC). Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activation was measured by conversion of L-arginine to L-citrulline in endothelial cells incubated with HDL from 49 subjects. Participants achieved an average weight loss of 2.2 ± 3.9 kg (P < 0.001), associated with reductions in both LDL-C (-6 ± 21 mg/dl, P = 0.004) and HDL-C (-3 ± 9 mg/dl, P = 0.016). Cholesterol efflux capacity by the ABCA1 transporter decreased by 10% (P = 0.006); efflux capacities by the ABCG1 and SR-B1 transporters were not significantly altered. ORAC decreased by 15% (P = 0.018); neither PON1 activity nor eNOS activation was significantly altered by reduction in HDL-C. Findings were similar for diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diet-induced weight loss in overweight or obese women is associated with a decrease in HDL-C levels, but overall HDL function is relatively spared, suggesting that decrease in HDL-C in this setting is not deleterious to cardiovascular risk.
Figures

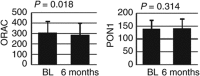
Similar articles
-
Impact of hormonal contraception and weight loss on high-density lipoprotein cholesterol efflux and lipoprotein particles in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2017 May;86(5):739-746. doi: 10.1111/cen.13310. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2017. PMID: 28199736 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bariatric surgery improves lipoprotein profile in morbidly obese patients by reducing LDL cholesterol, apoB, and SAA/PON1 ratio, increasing HDL cholesterol, but has no effect on cholesterol efflux capacity.J Clin Lipidol. 2018 Jan-Feb;12(1):193-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2017.10.007. Epub 2017 Nov 8. J Clin Lipidol. 2018. PMID: 29146227
-
Effects of diet and exercise in men and postmenopausal women with low levels of HDL cholesterol and high levels of LDL cholesterol.N Engl J Med. 1998 Jul 2;339(1):12-20. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199807023390103. N Engl J Med. 1998. PMID: 9647874 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of effects of long-term low-fat vs high-fat diets on blood lipid levels in overweight or obese patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2013 Dec;113(12):1640-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2013. PMID: 24139973 Review.
-
High-Density Lipoprotein Alterations in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity.Metabolites. 2023 Feb 9;13(2):253. doi: 10.3390/metabo13020253. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36837872 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dose-response relationship between physical activity and cardiometabolic risk in obese children and adolescents: A pre-post quasi-experimental study.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 19;14:1070653. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1070653. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36744040 Free PMC article.
-
Diets Low in Saturated Fat with Different Unsaturated Fatty Acid Profiles Similarly Increase Serum-Mediated Cholesterol Efflux from THP-1 Macrophages in a Population with or at Risk for Metabolic Syndrome: The Canola Oil Multicenter Intervention Trial.J Nutr. 2018 May 1;148(5):721-728. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxy040. J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30053283 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in weight loss and lipid profiles after a dietary purification program: a prospective case series.J Chiropr Med. 2013 Mar;12(1):30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2012.11.004. J Chiropr Med. 2013. PMID: 23997722 Free PMC article.
-
Cuban policosanol improves high-density lipoprotein cholesterol efflux capacity in healthy Japanese subjects.Front Nutr. 2024 Jan 8;10:1297008. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1297008. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38260075 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of hormonal contraception and weight loss on high-density lipoprotein cholesterol efflux and lipoprotein particles in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2017 May;86(5):739-746. doi: 10.1111/cen.13310. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2017. PMID: 28199736 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Tall AR. Cholesterol efflux pathways and other potential mechanisms involved in the athero-protective effect of high density lipoproteins. J Intern Med. 2008;263:256–273. - PubMed
-
- Mineo C, Deguchi H, Griffin JH, Shaul PW. Endothelial and antithrombotic actions of HDL. Circ Res. 2006;98:1352–1364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

