STING specifies IRF3 phosphorylation by TBK1 in the cytosolic DNA signaling pathway
- PMID: 22394562
- PMCID: PMC3549669
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2002521
STING specifies IRF3 phosphorylation by TBK1 in the cytosolic DNA signaling pathway
Abstract
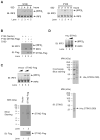
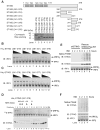
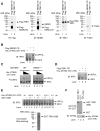
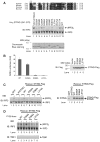
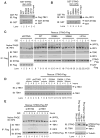
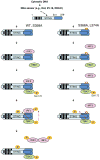
Cytosolic double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) stimulates the production of type I interferon (IFN) through the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident adaptor protein STING (stimulator of IFN genes), which activates the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3); however, how STING activates IRF3 is unclear. Here, we showed that STING stimulates phosphorylation of IRF3 by the kinase TBK1 (TANK-binding kinase 1) in an in vitro reconstitution system. With this system, we identified a carboxyl-terminal region of STING that was both necessary and sufficient to activate TBK1 and stimulate the phosphorylation of IRF3. We also found that STING interacted with both TBK1 and IRF3 and that mutations in STING that selectively disrupted its binding to IRF3 abrogated phosphorylation of IRF3 without impairing the activation of TBK1. These results suggest that STING functions as a scaffold protein to specify and promote the phosphorylation of IRF3 by TBK1. This scaffolding function of STING (and possibly of other adaptor proteins) may explain why IRF3 is activated in only a subset of signaling pathways that activate TBK1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The STING in the tail for cytosolic DNA-dependent activation of IRF3.Sci Signal. 2012 Mar 6;5(214):pe9. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002919. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22394560
-
Cytosolic-DNA-mediated, STING-dependent proinflammatory gene induction necessitates canonical NF-κB activation through TBK1.J Virol. 2014 May;88(10):5328-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00037-14. Epub 2014 Mar 5. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24600004 Free PMC article.
-
African Swine Fever Virus Armenia/07 Virulent Strain Controls Interferon Beta Production through the cGAS-STING Pathway.J Virol. 2019 May 29;93(12):e02298-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02298-18. Print 2019 Jun 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30918080 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanism of dsDNA sensing through the cGAS-STING pathway.Adv Immunol. 2024;162:1-21. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2024.02.003. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Adv Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38866436 Review.
-
Potential Therapeutic Value of the STING Inhibitors.Molecules. 2023 Mar 31;28(7):3127. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073127. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049889 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Innate immune recognition of DNA: A recent history.Virology. 2015 May;479-480:146-52. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.03.013. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Virology. 2015. PMID: 25816762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2024 Lasker Award Recipient Zhijian Chen elucidates how DNA stimulates immunity.J Clin Invest. 2024 Sep 19;134(19):e186104. doi: 10.1172/JCI186104. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39295301 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
cGAS-STING cytosolic DNA sensing pathway is suppressed by JAK2-STAT3 in tumor cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 31;11(1):7243. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86644-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33790360 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-induced Ordering of the C-terminal Tail Primes STING for Phosphorylation by TBK1.EBioMedicine. 2016 Jul;9:87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.05.039. Epub 2016 Jun 1. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27333035 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for nucleosome-mediated inhibition of cGAS activity.Cell Res. 2020 Dec;30(12):1088-1097. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-00422-4. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 33051594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takeuchi O, Akira S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 2010;140:805–820. - PubMed
-
- Yoneyama M, Fujita T. RNA recognition and signal transduction by RIG-I-like receptors. Immunol Rev. 2009;227:54–65. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Takahashi K, Sato S, Coban C, Kumar H, Kato H, Ishii KJ, Takeuchi O, Akira S. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:981–988. - PubMed
-
- Meylan E, Curran J, Hofmann K, Moradpour D, Binder M, Bartenschlager R, Tschopp J. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature. 2005;437:1167–1172. - PubMed
-
- Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Chen ZJ. Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3. Cell. 2005;122:669–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

