Colorectal Neoplasia Differentially Expressed (CRNDE), a Novel Gene with Elevated Expression in Colorectal Adenomas and Adenocarcinomas
- PMID: 22393467
- PMCID: PMC3278902
- DOI: 10.1177/1947601911431081
Colorectal Neoplasia Differentially Expressed (CRNDE), a Novel Gene with Elevated Expression in Colorectal Adenomas and Adenocarcinomas
Abstract
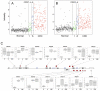
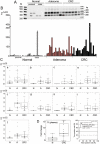
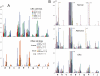
An uncharacterized gene locus (Chr16:hCG_1815491), now named colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed (gene symbol CRNDE), is activated early in colorectal neoplasia. The locus is unrelated to any known protein-coding gene. Microarray analysis of 454 tissue specimens (discovery) and 68 previously untested specimens (validation) showed elevated expression of CRNDE in >90% of colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas. These findings were confirmed and extended by exon microarray studies and RT-PCR assays. CRNDE transcription start sites were identified in CaCo2 and HCT116 cells by 5'-RACE. The major transcript isoforms in colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines and colorectal tissue are CRNDE-a, -b, -d, -e, -f, -h, and -j. Except for CRNDE-d, the known CRNDE splice variants are upregulated in neoplastic colorectal tissue; expression levels for CRNDE-h alone demonstrate a sensitivity of 95% and specificity of 96% for adenoma versus normal tissue. A quantitative RT-PCR assay measuring CRNDE-h RNA levels in plasma was (with a threshold of 2(-ΔCt) = 2.8) positive for 13 of 15 CRC patients (87%) but only 1 of 15 healthy individuals (7%). We conclude that individual CRNDE transcripts show promise as tissue and plasma biomarkers, potentially exhibiting high sensitivity and specificity for colorectal adenomas and cancers.
Keywords: CRNDE; RNA biomarker; colorectal adenoma; colorectal cancer; colorectal neoplasia.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: In relation to Clinical Genomics Pty. Ltd., S.K.P. and L.C.L. are employees with ownership interests, E.K.V. is a former employee, G.P.Y. is a paid consultant, and R.D. and P.L.M. received commercial research support from the company.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CRNDE: A Long Non-Coding RNA Involved in CanceR, Neurobiology, and DEvelopment.Front Genet. 2012 Nov 29;3:270. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00270. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 23226159 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and validation of molecular biomarkers for colorectal adenomas and cancer with application to blood testing.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029059. Epub 2012 Jan 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22276102 Free PMC article.
-
CRNDE, a long non-coding RNA responsive to insulin/IGF signaling, regulates genes involved in central metabolism.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1843(2):372-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.10.016. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24184209
-
CRNDE: an oncogenic long non-coding RNA in cancers.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 May 12;20:162. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01246-3. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32435153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRNDE: An important oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancers.Cell Prolif. 2018 Jun;51(3):e12440. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12440. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Cell Prolif. 2018. PMID: 29405523 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRNDE: A Long Non-Coding RNA Involved in CanceR, Neurobiology, and DEvelopment.Front Genet. 2012 Nov 29;3:270. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00270. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2012. PMID: 23226159 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC01296 is a potential prognostic biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer.Tumour Biol. 2015 Sep;36(9):7175-83. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3448-5. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25894381
-
SNHG7 is a lncRNA oncogene controlled by Insulin-like Growth Factor signaling through a negative feedback loop to tightly regulate proliferation.Sci Rep. 2020 May 22;10(1):8583. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65109-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32444795 Free PMC article.
-
Colorectal Adenomas-Genetics and Searching for New Molecular Screening Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 5;21(9):3260. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093260. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32380676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct regulatory functions and biological roles of lncRNA splice variants.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Mar 15;32:127-143. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.03.004. eCollection 2023 Jun 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 37025931 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stein U, Schlag PM. Clinical, biological, and molecular aspects of metastasis in colorectal cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2007;176:61-80 - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Atkin W, Lenz H-J, et al. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2010;375:1030-47 - PubMed
-
- Atkin WS, Edwards R, Kralj-Hans I, et al. UK Flexible Sigmoidoscopy Trial Investigators. Once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy screening in prevention of colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;375:1624-33 - PubMed
-
- Young GP. Population-based screening for colorectal cancer: Australian research and implementation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24(Suppl 3):S33-42 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
