Skin infection generates non-migratory memory CD8+ T(RM) cells providing global skin immunity
- PMID: 22388819
- PMCID: PMC3437663
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10851
Skin infection generates non-migratory memory CD8+ T(RM) cells providing global skin immunity
Abstract
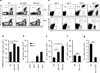
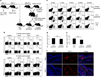
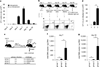
Protective T-cell memory has long been thought to reside in blood and lymph nodes, but recently the concept of immune memory in peripheral tissues mediated by resident memory T (T(RM)) cells has been proposed. Here we show in mice that localized vaccinia virus (VACV) skin infection generates long-lived non-recirculating CD8(+) skin T(RM) cells that reside within the entire skin. These skin T(RM) cells are potent effector cells, and are superior to circulating central memory T (T(CM)) cells at providing rapid long-term protection against cutaneous re-infection. We find that CD8(+) T cells are rapidly recruited to skin after acute VACV infection. CD8(+) T-cell recruitment to skin is independent of CD4(+) T cells and interferon-γ, but requires the expression of E- and P-selectin ligands by CD8(+) T cells. Using parabiotic mice, we further show that circulating CD8(+) T(CM) and CD8(+) skin T(RM) cells are both generated after skin infection; however, CD8(+) T(CM) cells recirculate between blood and lymph nodes whereas T(RM) cells remain in the skin. Cutaneous CD8(+) T(RM) cells produce effector cytokines and persist for at least 6 months after infection. Mice with CD8(+) skin T(RM) cells rapidly cleared a subsequent re-infection with VACV whereas mice with circulating T(CM) but no skin T(RM) cells showed greatly impaired viral clearance, indicating that T(RM) cells provide superior protection. Finally, we show that T(RM) cells generated as a result of localized VACV skin infection reside not only in the site of infection, but also populate the entire skin surface and remain present for many months. Repeated re-infections lead to progressive accumulation of highly protective T(RM) cells in non-involved skin. These findings have important implications for our understanding of protective immune memory at epithelial interfaces with the environment, and suggest novel strategies for vaccines that protect against tissue tropic organisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
T cell memory: Skin-deep memory.Nat Rev Immunol. 2012 Mar 22;12(4):230-1. doi: 10.1038/nri3201. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22437929 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Different patterns of peripheral migration by memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.Nature. 2011 Aug 14;477(7363):216-9. doi: 10.1038/nature10339. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21841802
-
Survival of tissue-resident memory T cells requires exogenous lipid uptake and metabolism.Nature. 2017 Mar 9;543(7644):252-256. doi: 10.1038/nature21379. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28219080 Free PMC article.
-
Central memory CD8+ T cells become CD69+ tissue-residents during viral skin infection independent of CD62L-mediated lymph node surveillance.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Mar 15;15(3):e1007633. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007633. eCollection 2019 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30875408 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and trafficking of CD8+ T cells during viral skin infection: immunological lessons learned from vaccinia virus.Curr Opin Virol. 2018 Feb;28:12-19. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Curr Opin Virol. 2018. PMID: 29080420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccinia Virus: Mechanisms Supporting Immune Evasion and Successful Long-Term Protective Immunity.Viruses. 2024 May 29;16(6):870. doi: 10.3390/v16060870. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TGF-β: Many Paths to CD103+ CD8 T Cell Residency.Cells. 2021 Apr 23;10(5):989. doi: 10.3390/cells10050989. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33922441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinetics of CD4+ T Helper and CD8+ Effector T Cell Responses in Acute Dengue Patients.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 24;11:1980. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01980. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33072068 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying Memory CD8 T Cells Reveals Regionalization of Immunosurveillance.Cell. 2015 May 7;161(4):737-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.031. Cell. 2015. PMID: 25957682 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells continuously patrol skin epithelia to quickly recognize local antigen.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 27;109(48):19739-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208927109. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23150545 Free PMC article.
-
Human epidermal Langerhans cells maintain immune homeostasis in skin by activating skin resident regulatory T cells.Immunity. 2012 May 25;36(5):873-84. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.018. Epub 2012 May 3. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22560445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conrad C, et al. α1β1 integrin is crucial for accumulation of epidermal T cells and the development of psoriasis. Nat Med. 2007;13:836–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

