Suppression of EGFR endocytosis by dynamin depletion reveals that EGFR signaling occurs primarily at the plasma membrane
- PMID: 22371560
- PMCID: PMC3311323
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1200164109
Suppression of EGFR endocytosis by dynamin depletion reveals that EGFR signaling occurs primarily at the plasma membrane
Abstract
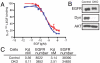
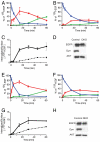
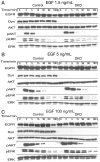
The role of endocytosis in the control of EGF receptor (EGFR) activation and cell signaling was explored by using mouse fibroblasts in which dynamin was conditionally depleted. Dynamin is a GTPase shown to play an important role in the control clathrin mediated endocytosis of EGFR and other cell surface receptors. In this report, we demonstrate that EGF binding activity and the display of high and low affinity EGFRs on the cell surface are not affected by dynamin depletion. By contrast, dynamin depletion leads to a strong inhibition of EGFR endocytosis, robust enhancement of EGFR autophosphorylation and ubiquitination, and slower kinetics of EGFR degradation. Surprisingly, MAPK stimulation induced by either low or high EGF concentrations is not affected by dynamin depletion. While a similar initial Akt response is detected in control or dynamin depleted fibroblasts, a somewhat more sustained Akt stimulation is detected in the dynamin depleted cells. These experiments demonstrate that dynamin-mediated endocytosis leads to attenuation of EGFR activation and degradation and that stimulation of the MAPK response and Akt activation are primarily mediated by activated EGFR located in the plasma membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Polyubiquitination of the epidermal growth factor receptor occurs at the plasma membrane upon ligand-induced activation.J Biol Chem. 2000 May 5;275(18):13940-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.18.13940. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10788520
-
High-affinity binding of epidermal growth factor (EGF) to EGF receptor is disrupted by overexpression of mutant dynamin (K44A).J Biol Chem. 1998 Jul 3;273(27):16639-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.27.16639. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9642213
-
Internalization mechanisms of the epidermal growth factor receptor after activation with different ligands.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058148. Epub 2013 Mar 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23472148 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting dynamin's role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Oct;37(Pt 5):1022-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0371022. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19754444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ErbBs.Exp Cell Res. 2008 Oct 15;314(17):3093-106. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.08.013. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Exp Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18793634 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoconjugation prolongs endosomal signaling of the epidermal growth factor receptor and enhances apoptosis.Nanoscale. 2016 Jul 14;8(28):13755-68. doi: 10.1039/c6nr02974d. Nanoscale. 2016. PMID: 27378391 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin S attenuates endosomal EGFR signalling: A mechanical rationale for the combination of cathepsin S and EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 8;6:29256. doi: 10.1038/srep29256. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27387133 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamin triple knockout cells reveal off target effects of commonly used dynamin inhibitors.J Cell Sci. 2013 Nov 15;126(Pt 22):5305-12. doi: 10.1242/jcs.138578. Epub 2013 Sep 17. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 24046449 Free PMC article.
-
NAADP-regulated two-pore channels drive phagocytosis through endo-lysosomal Ca2+ nanodomains, calcineurin and dynamin.EMBO J. 2020 Jul 15;39(14):e104058. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019104058. Epub 2020 Jun 8. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 32510172 Free PMC article.
-
Where EGF receptors transmit their signals.Sci Signal. 2012 Sep 25;5(243):pe41. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003341. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 23012653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carpenter G, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. - PubMed
-
- Sorkin A, Goh LK. Endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ErbBs. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315:683–696. - PubMed
-
- Sigismund S, et al. Clathrin-mediated internalization is essential for sustained EGFR signaling but dispensable for degradation. Dev Cell. 2008;15:209–219. - PubMed
-
- Vieira AV, Lamaze C, Schmid SL. Control of EGF receptor signaling by clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Science. 1996;274:2086–2089. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

