Retinoic acid signaling plays a restrictive role in zebrafish primitive myelopoiesis
- PMID: 22363502
- PMCID: PMC3281886
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030865
Retinoic acid signaling plays a restrictive role in zebrafish primitive myelopoiesis
Abstract
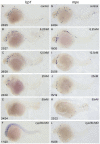
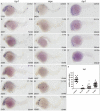
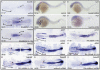
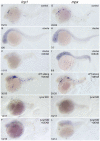
Retinoic acid (RA) is known to regulate definitive myelopoiesis but its role in vertebrate primitive myelopoiesis remains unclear. Here we report that zebrafish primitive myelopoiesis is restricted by RA in a dose dependent manner mainly before 11 hpf (hours post fertilization) when anterior hemangioblasts are initiated to form. RA treatment significantly reduces expressions of anterior hemangioblast markers scl, lmo2, gata2 and etsrp in the rostral end of ALPM (anterior lateral plate mesoderm) of the embryos. The result indicates that RA restricts primitive myelopoiesis by suppressing formation of anterior hemangioblasts. Analyses of ALPM formation suggest that the defective primitive myelopoiesis resulting from RA treatment before late gastrulation may be secondary to global loss of cells for ALPM fate whereas the developmental defect resulting from RA treatment during 10-11 hpf should be due to ALPM patterning shift. Overexpressions of scl and lmo2 partially rescue the block of primitive myelopoiesis in the embryos treated with 250 nM RA during 10-11 hpf, suggesting RA acts upstream of scl to control primitive myelopoiesis. However, the RA treatment blocks the increased primitive myelopoiesis caused by overexpressing gata4/6 whereas the abolished primitive myelopoiesis in gata4/5/6 depleted embryos is well rescued by 4-diethylamino-benzaldehyde, a retinal dehydrogenase inhibitor, or partially rescued by knocking down aldh1a2, the major retinal dehydrogenase gene that is responsible for RA synthesis during early development. Consistently, overexpressing gata4/6 inhibits aldh1a2 expression whereas depleting gata4/5/6 increases aldh1a2 expression. The results reveal that RA signaling acts downstream of gata4/5/6 to control primitive myelopoiesis. But, 4-diethylamino-benzaldehyde fails to rescue the defective primitive myelopoiesis in either cloche embryos or lycat morphants. Taken together, our results demonstrate that RA signaling restricts zebrafish primitive myelopoiesis through acting downstream of gata4/5/6, upstream of, or parallel to, cloche, and upstream of scl.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Retinoic Acid Signaling Is Essential for Valvulogenesis by Affecting Endocardial Cushions Formation in Zebrafish Embryos.Zebrafish. 2016 Feb;13(1):9-18. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2015.1117. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Zebrafish. 2016. PMID: 26671342
-
Zebrafish microRNA miR-210-5p inhibits primitive myelopoiesis by silencing foxj1b and slc3a2a mRNAs downstream of gata4/5/6 transcription factor genes.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 22;294(8):2732-2743. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005079. Epub 2018 Dec 28. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30593510 Free PMC article.
-
Ncor1 and Ncor2 play essential but distinct roles in zebrafish primitive myelopoiesis.Dev Dyn. 2014 Dec;243(12):1544-53. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24181. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Dev Dyn. 2014. PMID: 25156564
-
Patterning of vertebrate cardiac progenitor fields by retinoic acid signaling.Genesis. 2021 Nov;59(11):e23458. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23458. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Genesis. 2021. PMID: 34665508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesoderm patterning by a dynamic gradient of retinoic acid signalling.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Oct 12;375(1809):20190556. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0556. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32829679 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zebrafish Models for the Safety and Therapeutic Testing of Nanoparticles with a Focus on Macrophages.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jul 9;11(7):1784. doi: 10.3390/nano11071784. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34361170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoic acid catabolizing enzyme CYP26C1 is a genetic modifier in SHOX deficiency.EMBO Mol Med. 2016 Dec 1;8(12):1455-1469. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201606623. Print 2016 Dec. EMBO Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27861128 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish as a Model to Study Retinoic Acid Signaling in Development and Disease.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 15;11(4):1180. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041180. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcription factor Foxc1a in zebrafish directly regulates expression of nkx2.5, encoding a transcriptional regulator of cardiac progenitor cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jan 12;293(2):638-650. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000414. Epub 2017 Nov 21. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29162723 Free PMC article.
-
ALDH1A2-related disorder: A new genetic syndrome due to alteration of the retinoic acid pathway.Am J Med Genet A. 2023 Jan;191(1):90-99. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62991. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Am J Med Genet A. 2023. PMID: 36263470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galloway JL, Zon LI. Ontogeny of hematopoiesis: examining the emergence of hematopoietic cells in the vertebrate embryo. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2003;53:139–158. - PubMed
-
- Davidson AJ, Zon LI. The ‘definitive’ (and ‘primitive’) guide to zebrafish hematopoiesis. Oncogene. 2004;23:7233–7246. - PubMed
-
- Hsia N, Zon LI. Transcriptional regulation of hematopoietic stem cell development in zebrafish. Exp Hematol. 2005;33:1007–1014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

