Intermediate domain of receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) determines switch between necroptosis and RIPK1 kinase-dependent apoptosis
- PMID: 22362767
- PMCID: PMC3340215
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.288670
Intermediate domain of receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) determines switch between necroptosis and RIPK1 kinase-dependent apoptosis
Abstract
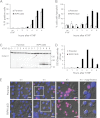
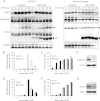
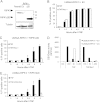
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) is an important component of the tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) signaling pathway. Depending on the cell type and conditions, RIPK1 mediates MAPK and NF-κB activation as well as cell death. Using a mutant form of RIPK1 (RIPK1ΔID) lacking the intermediate domain (ID), we confirm the requirement of this domain for activation of these signaling events. Moreover, expression of RIPK1ΔID resulted in enhanced recruitment of caspase-8 to the TNFR1 complex II component Fas-associated death domain (FADD), which allowed a shift from TNF-induced necroptosis to apoptosis in L929 cells. Addition of the RIPK1 kinase inhibitor necrostatin-1 strongly reduced recruitment of RIPK1 and caspase-8 to FADD and subsequent apoptosis, indicating a role for RIPK1 kinase activity in apoptotic complex formation. Our study shows that RIPK1 has an anti-apoptotic function residing in its ID and demonstrates a cellular system as an elegant genetic model for RIPK1 kinase-dependent apoptosis that, in contrast to the Smac mimetic model, does not rely on depletion of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 and 2 (cIAP1/2).
Figures


Similar articles
-
RIPK3 contributes to TNFR1-mediated RIPK1 kinase-dependent apoptosis in conditions of cIAP1/2 depletion or TAK1 kinase inhibition.Cell Death Differ. 2013 Oct;20(10):1381-92. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.94. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Cell Death Differ. 2013. PMID: 23892367 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming cancer cell resistance to Smac mimetic induced apoptosis by modulating cIAP-2 expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 29;107(26):11936-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005667107. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20547836 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-Mediated Regulation of RIPK1 Kinase Activity Independent of IKK and MK2.Mol Cell. 2018 Feb 15;69(4):566-580.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.027. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29452637 Free PMC article.
-
Holding RIPK1 on the Ubiquitin Leash in TNFR1 Signaling.Trends Cell Biol. 2016 Jun;26(6):445-461. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Trends Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26877205 Review.
-
Targeting RIPK1 kinase for modulating inflammation in human diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 8;14:1159743. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1159743. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969188 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death.Cell Mol Immunol. 2021 May;18(5):1106-1121. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00630-3. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33785842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis in osteosarcoma treatment.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):44763-44778. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8206. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27007056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
K45A mutation of RIPK1 results in poor necroptosis and cytokine signaling in macrophages, which impacts inflammatory responses in vivo.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Oct;23(10):1628-37. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.51. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 27258786 Free PMC article.
-
Eleostearic acid induces RIP1-mediated atypical apoptosis in a kinase-independent manner via ERK phosphorylation, ROS generation and mitochondrial dysfunction.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Jun 20;4(6):e674. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.188. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23788031 Free PMC article.
-
RIPK1- and RIPK3-induced cell death mode is determined by target availability.Cell Death Differ. 2014 Oct;21(10):1600-12. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.70. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Cell Death Differ. 2014. PMID: 24902899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson N. S., Dixit V., Ashkenazi A. (2009) Death receptor signal transducers: Nodes of coordination in immune signaling networks. Nat. Immunol. 10, 348–355 - PubMed
-
- Micheau O., Tschopp J. (2003) Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 114, 181–190 - PubMed
-
- Schneider-Brachert W., Tchikov V., Neumeyer J., Jakob M., Winoto-Morbach S., Held-Feindt J., Heinrich M., Merkel O., Ehrenschwender M., Adam D., Mentlein R., Kabelitz D., Schütze S. (2004) Compartmentalization of TNF receptor 1 signaling: Internalized TNF receptosomes as death signaling vesicles. Immunity 21, 415–428 - PubMed
-
- Wajant H., Scheurich P. (2011) TNFR1-induced activation of the classical NF-κB pathway. FEBS. J. 278, 862–876 - PubMed
-
- Ea C. K., Deng L., Xia Z. P., Pineda G., Chen Z. J. (2006) Activation of IKK by TNFα requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol. Cell 22, 245–257 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

