Up-regulation of miR-210 by vascular endothelial growth factor in ex vivo expanded CD34+ cells enhances cell-mediated angiogenesis
- PMID: 22360314
- PMCID: PMC3823435
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01557.x
Up-regulation of miR-210 by vascular endothelial growth factor in ex vivo expanded CD34+ cells enhances cell-mediated angiogenesis
Abstract
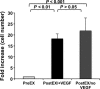
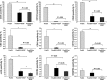
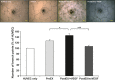
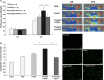
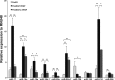
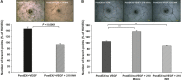
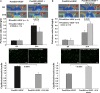
Ex vivo culture has been proposed as a means to augment and repair autologous cells in patients with chronic diseases, but the mechanisms governing improvement in cell function are not well understood. Although microRNAs (miRs) are increasingly appreciated as key regulators of cellular function, a role for these factors in CD34+ cell-mediated angiogenesis has not been elucidated. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was previously shown to induce expression of certain miRs associated with angiogenesis in endothelial cells and promote survival and number of vascular colony forming units of haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). We sought to evaluate the role of VEGF in expansion and angiogenic function of CD34+ cells and to identify specific miRs associated with angiogenic properties of expanded cells. Umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells were effectively expanded (18- to 22-fold) in culture medium containing stem cell factor (SCF), Flt-3 ligand (Flt-3), thrombopoietin (TPO) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) with (postEX/+VEGF) and without VEGF (postEX/noVEGF). Tube formation in matrigel assay and tissue perfusion/capillary density in mice ischaemic hindlimb were significantly improved by postEX/+VEGF cells compared with fresh CD34+ and postEX/noVEGF cells. MiR-210 expression was significantly up-regulated in postEX/+VEGF cells. MiR-210 inhibitor abrogated and 210 mimic recapitulated the pro-angiogenic effects by treatment of postEX/+VEGF and postEX/noVEGF cells respectively. Collectively, these observations highlight a critical role for VEGF in enhancing the angiogenic property of expanded cells, and identify miR-210 as a potential therapeutic target to enhance CD34+ stem cell function for the treatment of ischaemic vascular disease.
© 2012 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2012 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Angiogenic Mechanisms of Human CD34+ Stem Cell Exosomes in the Repair of Ischemic Hindlimb.Circ Res. 2017 Apr 28;120(9):1466-1476. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.310557. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28298297 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin improves the angiogenic potential of human CD34⁺ cells co-incident with downregulating CXCL10 and TIMP1 gene expression and increasing VEGFA under hyperglycemia and hypoxia within a therapeutic window for myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016 Feb 9;15:27. doi: 10.1186/s12933-016-0344-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016. PMID: 26861446 Free PMC article.
-
Successful short-term ex vivo expansion of NOD/SCID repopulating ability and CAFC week 6 from umbilical cord blood.Leukemia. 2000 Nov;14(11):1944-53. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401917. Leukemia. 2000. PMID: 11069030
-
microRNA-200b as a Switch for Inducible Adult Angiogenesis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 May 10;22(14):1257-72. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.6065. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015. PMID: 25761972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor in heart failure.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013 Sep;10(9):519-30. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2013.94. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23856679 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Significance of MicroRNAs in Glioma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Mar 26;2019:4015969. doi: 10.1155/2019/4015969. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31032345 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Regulation of Circulating microRNAs During Acute Exercise and Long-Term Exercise Training in Basketball Athletes.Front Physiol. 2018 Mar 26;9:282. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00282. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29662456 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible miR-210 contributes to preeclampsia via targeting thrombospondin type I domain containing 7A.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 22;6:19588. doi: 10.1038/srep19588. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26796133 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated expression of miR-210 predicts poor survival of cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 20;9(2):e89223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089223. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-377 regulates mesenchymal stem cell-induced angiogenesis in ischemic hearts by targeting VEGF.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 24;9(9):e104666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104666. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25251394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275:964–7. - PubMed
-
- Shantsila E, Watson T, Lip GYH. Endothelial progenitor cells in cardiovascular disorders. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:741–52. - PubMed
-
- Bushati N, Cohen SM. microRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:175–205. - PubMed
-
- Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C, Pober JS, et al. Dicer dependent microRNAs regulate gene expression and functions in human endothelial cells. Circ Res. 2007;100:1164–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

