Overlapping functions between XLF repair protein and 53BP1 DNA damage response factor in end joining and lymphocyte development
- PMID: 22355127
- PMCID: PMC3309750
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1120160109
Overlapping functions between XLF repair protein and 53BP1 DNA damage response factor in end joining and lymphocyte development
Abstract
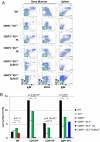
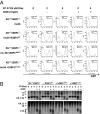
Nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ), a major pathway of DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair, is required during lymphocyte development to resolve the programmed DSBs generated during Variable, Diverse, and Joining [V(D)J] recombination. XRCC4-like factor (XLF) (also called Cernunnos or NHEJ1) is a unique component of the NHEJ pathway. Although germ-line mutations of other NHEJ factors abrogate lymphocyte development and lead to severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), XLF mutations cause a progressive lymphocytopenia that is generally less severe than SCID. Accordingly, XLF-deficient murine lymphocytes show no measurable defects in V(D)J recombination. We reported earlier that ATM kinase and its substrate histone H2AX are both essential for V(D)J recombination in XLF-deficient lymphocytes, despite moderate role in V(D)J recombination in WT cells. p53-binding protein 1 (53BP1) is another substrate of ATM. 53BP1 deficiency led to small reduction of peripheral lymphocyte number by compromising both synapse and end-joining at modest level during V(D)J recombination. Here, we report that 53BP1/XLF double deficiency blocks lymphocyte development at early progenitor stages, owing to severe defects in end joining during chromosomal V(D)J recombination. The unrepaired DNA ends are rapidly degraded in 53BP1(-/-)XLF(-/-) cells, as reported for H2AX(-/-)XLF(-/-) cells, revealing an end protection role for 53BP1 reminiscent of H2AX. In contrast to the early embryonic lethality of H2AX(-/-)XLF(-/-) mice, 53BP1(-/-)XLF(-/-) mice are born alive and develop thymic lymphomas with translocations involving the T-cell receptor loci. Together, our findings identify a unique function for 53BP1 in end-joining and tumor suppression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ATM damage response and XLF repair factor are functionally redundant in joining DNA breaks.Nature. 2011 Jan 13;469(7329):250-4. doi: 10.1038/nature09604. Epub 2010 Dec 15. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21160472 Free PMC article.
-
Functional redundancy between repair factor XLF and damage response mediator 53BP1 in V(D)J recombination and DNA repair.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Feb 14;109(7):2455-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121458109. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22308489 Free PMC article.
-
Defective DNA repair and increased genomic instability in Cernunnos-XLF-deficient murine ES cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Mar 13;104(11):4518-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611734104. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360556 Free PMC article.
-
Functional overlaps between XLF and the ATM-dependent DNA double strand break response.DNA Repair (Amst). 2014 Apr;16:11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Feb 20. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014. PMID: 24674624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
XLF/Cernunnos: An important but puzzling participant in the nonhomologous end joining DNA repair pathway.DNA Repair (Amst). 2017 Oct;58:29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 18. DNA Repair (Amst). 2017. PMID: 28846869 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Paralogue of XRCC4 and XLF in DNA Damage Repair and Cancer Development.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 2;13:852453. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.852453. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetyltransferases GCN5 and PCAF Are Required for B Lymphocyte Maturation in Mice.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 31;12(1):61. doi: 10.3390/biom12010061. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 35053209 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into NHEJ: building up an integrated picture of the dynamic DSB repair super complex, one component and interaction at a time.DNA Repair (Amst). 2014 May;17:110-20. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Mar 20. DNA Repair (Amst). 2014. PMID: 24656613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The (Lack of) DNA Double-Strand Break Repair Pathway Choice During V(D)J Recombination.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 5;12:823943. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.823943. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35082840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multivalent interactions of the disordered regions of XLF and XRCC4 foster robust cellular NHEJ and drive the formation of ligation-boosting condensates in vitro.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Nov;31(11):1732-1744. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01339-x. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38898102
References
-
- Rooney S, Chaudhuri J, Alt FW. The role of the non-homologous end-joining pathway in lymphocyte development. Immunol Rev. 2004;200:115–131. - PubMed
-
- Ahnesorg P, Smith P, Jackson SP. XLF interacts with the XRCC4-DNA ligase IV complex to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Cell. 2006;124:301–313. - PubMed
-
- Buck D, et al. Cernunnos, a novel nonhomologous end-joining factor, is mutated in human immunodeficiency with microcephaly. Cell. 2006;124:287–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

