The HSP90 inhibitor XL888 overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance mediated through diverse mechanisms
- PMID: 22351686
- PMCID: PMC3398738
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2612
The HSP90 inhibitor XL888 overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance mediated through diverse mechanisms
Abstract
Purpose: The clinical use of BRAF inhibitors is being hampered by the acquisition of drug resistance. This study shows the potential therapeutic use of the HSP90 inhibitor (XL888) in six different models of vemurafenib resistance.
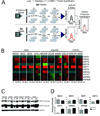
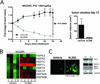
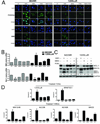
Experimental design: The ability of XL888 to inhibit growth and to induce apoptosis and tumor regression of vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cell lines was shown in vitro and in vivo. A novel mass spectrometry-based pharmacodynamic assay was developed to measure intratumoral HSP70 levels following HSP90 inhibition in melanoma cell lines, xenografts, and melanoma biopsies. Mechanistic studies were carried out to determine the mechanism of XL888-induced apoptosis.
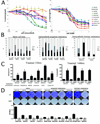
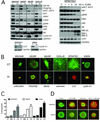
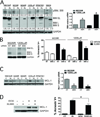
Results: XL888 potently inhibited cell growth, induced apoptosis, and prevented the growth of vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cell lines in 3-dimensional cell culture, long-term colony formation assays, and human melanoma mouse xenografts. The reversal of the resistance phenotype was associated with the degradation of PDGFRβ, COT, IGFR1, CRAF, ARAF, S6, cyclin D1, and AKT, which in turn led to the nuclear accumulation of FOXO3a, an increase in BIM (Bcl-2 interacting mediator of cell death) expression, and the downregulation of Mcl-1. In most resistance models, XL888 treatment increased BIM expression, decreased Mcl-1 expression, and induced apoptosis more effectively than dual mitogen-activated protein-extracellular signal-regulated kinase/phosphoinositide 3-kinase (MEK/PI3K) inhibition.
Conclusions: HSP90 inhibition may be a highly effective strategy at managing the diverse array of resistance mechanisms being reported to BRAF inhibitors and appears to be more effective at restoring BIM expression and downregulating Mcl-1 expression than combined MEK/PI3K inhibitor therapy.
©2012 AACR.
Figures
Comment in
-
Will Hsp90 inhibitors prove effective in BRAF-mutant melanomas?Clin Cancer Res. 2012 May 1;18(9):2420-2. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0626. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22442059
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Wee1, AKT, and CDK4 underlies the efficacy of the HSP90 inhibitor XL888 in an in vivo model of NRAS-mutant melanoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Jun;12(6):901-12. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-1003. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23538902 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating melanoma drug response and therapeutic escape with quantitative proteomics.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Jul;13(7):1844-54. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.037424. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24760959 Free PMC article.
-
The Novel ATP-Competitive MEK/Aurora Kinase Inhibitor BI-847325 Overcomes Acquired BRAF Inhibitor Resistance through Suppression of Mcl-1 and MEK Expression.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Jun;14(6):1354-64. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0832. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 25873592 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to Raf inhibition in cancer.Drug Discov Today Technol. 2014 Mar;11:27-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2013.12.004. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2014. PMID: 24847650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Navigating the therapeutic complexity of PI3K pathway inhibition in melanoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Oct 1;19(19):5310-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0142. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24089444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resistance to HSP90 inhibition involving loss of MCL1 addiction.Oncogene. 2016 Mar 24;35(12):1483-92. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.213. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26096930 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer can be delayed by an upfront combination with the HSP90 inhibitor onalespib.Br J Cancer. 2016 Oct 25;115(9):1069-1077. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.294. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Br J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27673365 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the RAS/RAF/MAPK pathway for cancer therapy: from mechanism to clinical studies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Dec 18;8(1):455. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01705-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 38105263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging transcriptional dynamics to improve BRAF inhibitor responses in melanoma.EBioMedicine. 2019 Oct;48:178-190. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.09.023. Epub 2019 Oct 5. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31594749 Free PMC article.
-
The antimelanoma activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589) is mediated by direct tumor cytotoxicity and increased tumor immunogenicity.Melanoma Res. 2013 Oct;23(5):341-8. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0b013e328364c0ed. Melanoma Res. 2013. PMID: 23963286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smalley KS, Sondak VK. Melanoma--an unlikely poster child for personalized cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:876–878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

