Role of fibroblast growth factor receptors in astrocytic stem cells
- PMID: 22347841
- PMCID: PMC3279755
- DOI: 10.2174/157436212799278205
Role of fibroblast growth factor receptors in astrocytic stem cells
Abstract
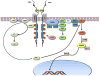
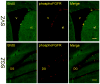
There are two well-defined neurogenic regions in the adult brain, the subventricular zone (SVZ) lining the lateral wall of the lateral ventricles and, the subgranular zone (SGZ) in the dentate gyrus at the hippocampus. Within these neurogenic regions, there are neural stem cells with astrocytic characteristics, which actively respond to the basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF, FGF2 or FGF-β) by increasing their proliferation, survival and differentiation, both in vivo and in vitro. FGF2 binds to fibroblast growth factor receptors 1 to 4 (FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4). Interestingly, these receptors are differentially expressed in neurogenic progenitors. During development, FGFR-1 and FGFR-2 drive oligodendrocytes and motor neuron specification. In particular, FGFR-1 determines oligodendroglial and neuronal cell fate, whereas FGFR-2 is related to oligodendrocyte specification. In the adult SVZ, FGF-2 promotes oligodendrogliogenesis and myelination. FGF-2 deficient mice show a reduction in the number of new neurons in the SGZ, which suggests that FGFR-1 is important for neuronal cell fate in the adult hippocampus. In human brain, FGF-2 appears to be an important component in the anti-depressive effect of drugs. In summary, FGF2 is an important modulator of the cell fate of neural precursor and, promotes oligodendrogenesis. In this review, we describe the expression pattern of FGFR2 and its role in neural precursors derived from the SVZ and the SGZ.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diphenylhydantoin promotes proliferation in the subventricular zone and dentate gyrus.Am J Neurosci. 2012 Mar 6;3(1):1-9. doi: 10.3844/amjnsp.2012.1.9. Am J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 24478822 Free PMC article.
-
The FGF-2/FGFRs neurotrophic system promotes neurogenesis in the adult brain.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009 Aug;116(8):995-1005. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0207-z. Epub 2009 Mar 17. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009. PMID: 19291360 Review.
-
Acute intermittent nicotine treatment induces fibroblast growth factor-2 in the subventricular zone of the adult rat brain and enhances neuronal precursor cell proliferation.Neuroscience. 2007 Mar 16;145(2):470-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.12.012. Epub 2006 Dec 16. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17241745
-
Cytoarchitecture of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR-2) immunoreactivity in astrocytes of neurogenic and non-neurogenic regions of the young adult and aged rat brain.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Sep 1;498(1):1-15. doi: 10.1002/cne.21009. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16856175
-
The role of EGFR and ErbB family related proteins in the oligodendrocyte specification in germinal niches of the adult mammalian brain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Dec 17;7:258. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00258. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24381541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor protects C17.2 cells from radiation-induced injury through ERK1/2.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Sep;18(9):767-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00365.x. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012. PMID: 22943143 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Targets in Synovial Sarcoma: A Mini-Review.Front Oncol. 2019 Oct 18;9:1078. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01078. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31681608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Effects of Ionizing Radiation on the Hippocampus: Linking Effects of the Sonic Hedgehog Pathway Activation with Radiation Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;22(22):12605. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212605. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830484 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal astrocytic FGFR3 activation leads to mechanical hypersensitivity by increased TNF-α in spared nerve injury.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Aug 1;12(8):2898-2908. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31934126 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of Growth Factors in Autism and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2017 Jul 13;8:126. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00126. eCollection 2017. Front Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28751869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mackay-Sim A. Stem cells and their niche in the adult olfactory mucosa. Arch Ital Biol. 2010 Jun;148(2):47–58. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Verdugo JM, Doetsch F, Wichterle H, Lim DA, Alvarez-Buylla A. Architecture and cell types of the adult subventricular zone: in search of the stem cells. J Neurobiol. 1998 Aug;36(2):234–48. - PubMed
-
- Seri B, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Collado-Morente L, McEwen BS, Alvarez-Buylla A. Cell types, lineage, and architecture of the germinal zone in the adult dentate gyrus. The Journal of comparative neurology. 2004 Oct 25;478(4):359–78. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
