Regulation of NF-κB signaling by the A20 deubiquitinase
- PMID: 22343828
- PMCID: PMC3532050
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2011.59
Regulation of NF-κB signaling by the A20 deubiquitinase
Abstract
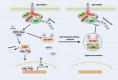
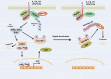
The NF-κB transcription factor is a central mediator of inflammatory and innate immune signaling pathways. Activation of NF-κB is achieved by K63-linked polyubiquitination of key signaling molecules which recruit kinase complexes that in turn activate the IκB kinase (IKK). Ubiquitination is a highly dynamic process and is balanced by deubiquitinases that cleave polyubiquitin chains and terminate downstream signaling events. The A20 deubiquitinase is a critical negative regulator of NF-κB and inflammation, since A20-deficient mice develop uncontrolled and spontaneous multi-organ inflammation. Furthermore, specific polymorphisms in the A20 genomic locus predispose humans to autoimmune disease. Recent studies also indicate that A20 is an important tumor suppressor that is inactivated in B-cell lymphomas. Therefore, targeting A20 may form the basis of novel therapies for autoimmune disease and lymphomas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression, biological activities and mechanisms of action of A20 (TNFAIP3).Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Dec 15;80(12):2009-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.044. Epub 2010 Jul 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20599425 Review.
-
Specific recognition of linear polyubiquitin by A20 zinc finger 7 is involved in NF-κB regulation.EMBO J. 2012 Oct 3;31(19):3856-70. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.241. Epub 2012 Aug 28. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 23032187 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of the A20/ABIN-mediated inhibition of NF-κB signaling via modifying the ubiquitinated proteins in a basal chordate.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 May 6;111(18):6720-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1321187111. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24753567 Free PMC article.
-
The kinase IKKα inhibits activation of the transcription factor NF-κB by phosphorylating the regulatory molecule TAX1BP1.Nat Immunol. 2011 Jul 17;12(9):834-43. doi: 10.1038/ni.2066. Nat Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21765415 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of NF-κB by deubiquitinases.Immunol Rev. 2012 Mar;246(1):107-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01100.x. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22435550 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation of Biomarker Expression in Colonic Mucosa with Disease Phenotype in Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Oct;60(10):2976-84. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3700-2. Epub 2015 May 9. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25956706 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kB signaling in myeloid cells mediates the pathogenesis of immune-mediated nephritis.J Autoimmun. 2019 Mar;98:33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.11.004. Epub 2019 Jan 3. J Autoimmun. 2019. PMID: 30612857 Free PMC article.
-
The Oxidative Balance Orchestrates the Main Keystones of the Functional Activity of Cardiomyocytes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jan 10;2022:7714542. doi: 10.1155/2022/7714542. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35047109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acquired deficiency of A20 results in rapid apoptosis, systemic inflammation, and abnormal hematopoietic stem cell function.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 31;9(1):e87425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087425. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24498102 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB in inflammation and renal diseases.Cell Biosci. 2015 Nov 16;5:63. doi: 10.1186/s13578-015-0056-4. eCollection 2015. Cell Biosci. 2015. PMID: 26579219 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–362. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Signaling to NF-κB. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Hacker H, Karin M. Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases. Sci STKE. 2006;2006:re13. - PubMed
-
- Sun SC, Ganchi PA, Ballard DW, Greene WC. NF-κB controls expression of inhibitor IκBα: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science. 1993;259:1912–1915. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

