Use of 5-cyano-2,3-ditolyl-tetrazolium chloride staining as an indicator of biocidal activity in a rapid assay for anti-Acanthamoeba agents
- PMID: 22337974
- PMCID: PMC3347101
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.06461-11
Use of 5-cyano-2,3-ditolyl-tetrazolium chloride staining as an indicator of biocidal activity in a rapid assay for anti-Acanthamoeba agents
Abstract
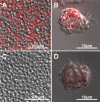
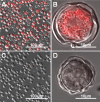
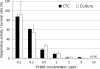
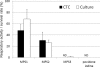
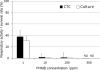
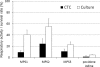
The usefulness of 5-cyano-2,3-ditolyl-tetrazolium chloride (CTC) staining to determine the respiratory activity of Acanthamoeba was evaluated in this study. Acanthamoeba trophozoites and cysts have a red fluorescence after staining with CTC. To determine the effectiveness of CTC staining as a CTC biocidal assay for Acanthamoeba, the trophozoites and cysts of Acanthamoeba castellanii (ATCC 5037) were treated with serial concentrations of disinfectant solutions, namely, polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB) and commercial soft contact lens (SCL) disinfectant solutions. The treated Acanthamoeba organisms were stained with CTC, and their respiratory activity was determined by the intensity of fluorescence in a fluorescence microplate reader. The survival rates of the same samples were determined by a culture-dependent biocidal assay using the Spearman-Karber method. Our results showed that the respiratory activities determined by the CTC biocidal assay and the survival rates determined by the culture-dependent biocidal assay for Acanthamoeba trophozoites and cysts decreased in a dose-dependent way after PHMB treatments, and the results were significantly correlated (r = 0.83 and P < 0.01 for trophozoites; r = 0.60 and P < 0.01 for cysts; Spearman rank correlation test). The respiratory activities in the trophozoites and cysts treated with SCL disinfectant solutions were significantly correlated with the survival rate (r = 0.70 and P < 0.01 for trophozoites; r = 0.64 and P < 0.01 for cysts; Spearman rank correlation test). The significant correlation of the results indicated that the CTC biocidal assay can be used as an alternative method to a culture-dependent biocidal assay. The CTC biocidal assay is a rapid and simple method to test the effectiveness of disinfectant solutions against Acanthamoeba trophozoites and cysts.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of in vitro assays to study the effectiveness of antiparasitics against Acanthamoeba castellani trophozoites and cysts.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2019 Dec 13;67(1):23-32. doi: 10.1556/030.66.2019.029. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2019. PMID: 31833381
-
Development of standardized methods for assessing biocidal efficacy of contact lens care solutions against Acanthamoeba trophozoites and cysts.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Jul 5;54(7):4527-37. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-11927. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23745008
-
In vitro Evaluation the Efficacy of Some New Plant Extracts and Biocides on the Viability of Acanthamoeba castellanii.Protist. 2023 Jun;174(3):125966. doi: 10.1016/j.protis.2023.125966. Epub 2023 May 9. Protist. 2023. PMID: 37229821
-
Methods used to evaluate the effectiveness of contact lens care solutions and other compounds against Acanthamoeba: a review of the literature.CLAO J. 2000 Apr;26(2):72-84. CLAO J. 2000. PMID: 10810937 Review.
-
Phenotype microarray technology and its application in industrial biotechnology.Biotechnol Lett. 2014 Jun;36(6):1153-60. doi: 10.1007/s10529-014-1481-x. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Biotechnol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24563312 Review.
Cited by
-
Honokiol induces superoxide production by targeting mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I in Candida albicans.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 30;12(8):e0184003. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184003. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28854218 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Metal Chelation by a Thiosemicarbazone Derivative Interferes with Mitochondrial Respiration and Ribosome Biogenesis in Candida albicans.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0195121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01951-21. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35412374 Free PMC article.
-
Artemether Exhibits Amoebicidal Activity against Acanthamoeba castellanii through Inhibition of the Serine Biosynthesis Pathway.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Aug;59(8):4680-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04758-14. Epub 2015 May 26. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26014935 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and identification of BP100 peptide conjugates active against Xylella fastidiosa using a viability-qPCR method.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Jul 29;20(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01915-3. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32727358 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and expression of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase and phosphoserine aminotransferase in the serine biosynthetic pathway from Acanthamoeba castellanii.Parasitol Res. 2015 Apr;114(4):1387-95. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4317-2. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Parasitol Res. 2015. PMID: 25622549
References
-
- Borazjani RN, Kilvington S. 2005. Efficacy of multipurpose solutions against Acanthamoeba species. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 28:169–175 - PubMed
-
- Catala P, et al. 1999. Effectiveness of CSE to counterstain particles and dead bacterial cells with permeabilised membranes: application to viability assessment in waters. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 178:219–226 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

