Antitumor effect of berberine against primary effusion lymphoma via inhibition of NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 22320346
- PMCID: PMC7659260
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02212.x
Antitumor effect of berberine against primary effusion lymphoma via inhibition of NF-κB pathway
Abstract
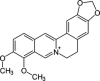
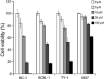
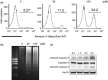
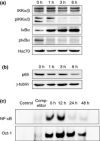
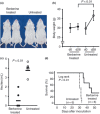
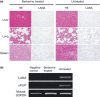
Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) is an infrequent and distinct entity among the aggressive non-Hodgkin B cell lymphomas that occurs predominantly in patients with advanced AIDS. It shows serous lymphomatous effusion in body cavities, and is resistant to conventional chemotherapy with a poor prognosis. Thus, the optimal treatment for PEL is not well defined and there is a need for novel agents. PEL has been recognized as the tumor caused by Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus/human herpes virus-8 (KSHV/HHV-8), and nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation plays a critical role in the survival and growth of PEL cells. In this study, we assessed the antitumor effect of berberine, a naturally occurring isoquinoline alkaloid, on this pathway. The methylthiotetrazole assay showed that cell proliferation in the PEL cell lines was inhibited by berberine. Berberine also induced caspase-dependent apoptosis and suppressed NF-κB activity by inhibiting IκB kinase (IKK) phosphorylation, IκB phosphorylation and IκB degradation, upstream targets of the NF-κB pathway, in PEL cells. In a xenograft mouse model that showed ascites and diffuse organ invasion of PEL cells, treatment with berberine inhibited the growth and invasion of PEL cells significantly compared with untreated mice. These results show that the suppression of NF-κB is a molecular target for treating PEL, and berberine is a potential antitumor agent for PEL.
© 2012 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Current status of treatment for primary effusion lymphoma.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2014 Aug;3(3):65-74. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2014.01010. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2014. PMID: 25364646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biscoclaurine alkaloid cepharanthine inhibits the growth of primary effusion lymphoma in vitro and in vivo and induces apoptosis via suppression of the NF-kappaB pathway.Int J Cancer. 2009 Sep 15;125(6):1464-72. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24521. Int J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19521981
-
Diethyldithiocarbamate induces apoptosis in HHV-8-infected primary effusion lymphoma cells via inhibition of the NF-κB pathway.Int J Oncol. 2012 Apr;40(4):1071-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1313. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22200846 Free PMC article.
-
A purine scaffold HSP90 inhibitor BIIB021 has selective activity against KSHV-associated primary effusion lymphoma and blocks vFLIP K13-induced NF-κB.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 15;19(18):5016-26. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3510. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23881928 Free PMC article.
-
Human Herpesvirus Type 8-associated Large B-cell Lymphoma: A Nonserous Extracavitary Variant of Primary Effusion Lymphoma in an HIV-infected Man: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2016 Jun;16(6):311-21. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2016.03.013. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2016. PMID: 27234438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Berberine derivatives with a long alkyl chain branched by hydroxyl group and methoxycarbonyl group at 9-position show improved anti-proliferation activity and membrane permeability in A549 cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020 Jun;41(6):813-824. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0346-1. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020. PMID: 31949294 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of treatment for primary effusion lymphoma.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2014 Aug;3(3):65-74. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2014.01010. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2014. PMID: 25364646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MKK4 Inhibitors-Recent Development Status and Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 19;24(8):7495. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087495. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alkaloid from Alstonia yunnanensis diels root against gastrointestinal cancer: Acetoxytabernosine inhibits apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 11;13:1085309. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1085309. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36712668 Free PMC article.
-
Nm23-H1 induces apoptosis in primary effusion lymphoma cells via inhibition of NF-κB signaling through interaction with oncogenic latent protein vFLIP K13 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022 Oct;45(5):967-989. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00701-9. Epub 2022 Aug 14. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 35964258
References
-
- Ansari MQ, Dawson DB, Nador R et al Primary body cavity‐based AIDS‐related lymphomas. Am J Clin Pathol 1996; 105: 221–9. - PubMed
-
- Nador RG, Cesarman E, Chadburn A et al Primary effusion lymphoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity associated with the Kaposi's sarcoma‐associated herpes virus. Blood 1996; 88: 645–56. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM. Kaposi's sarcoma‐associated herpesvirus‐like DNA sequences in AIDS‐related body‐cavity‐based lymphomas. N Engl J Med 1995; 332: 1186–91. - PubMed
-
- Keller SA, Schattner EJ, Cesarman E. Inhibition of NF‐kappaB induces apoptosis of KSHV‐infected primary effusion lymphoma cells. Blood 2000; 96: 2537–42. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Feldman GM, Tosato G. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and decreases survivin expression in primary effusion lymphoma. Blood 2003; 101: 1535–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

