Cdc73 subunit of Paf1 complex contains C-terminal Ras-like domain that promotes association of Paf1 complex with chromatin
- PMID: 22318720
- PMCID: PMC3322841
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.325647
Cdc73 subunit of Paf1 complex contains C-terminal Ras-like domain that promotes association of Paf1 complex with chromatin
Abstract
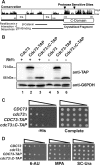
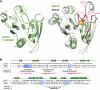
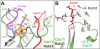
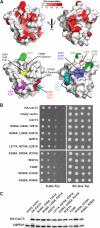
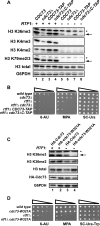
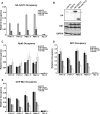
The conserved Paf1 complex localizes to the coding regions of genes and facilitates multiple processes during transcription elongation, including the regulation of histone modifications. However, the mechanisms that govern Paf1 complex recruitment to active genes are undefined. Here we describe a previously unrecognized domain within the Cdc73 subunit of the Paf1 complex, the Cdc73 C-domain, and demonstrate its importance for Paf1 complex occupancy on transcribed chromatin. Deletion of the C-domain causes phenotypes associated with elongation defects without an apparent loss of complex integrity. Simultaneous mutation of the C-domain and another subunit of the Paf1 complex, Rtf1, causes enhanced mutant phenotypes and loss of histone H3 lysine 36 trimethylation. The crystal structure of the C-domain reveals unexpected similarity to the Ras family of small GTPases. Instead of a deep nucleotide-binding pocket, the C-domain contains a large but comparatively flat surface of highly conserved residues, devoid of ligand. Deletion of the C-domain results in reduced chromatin association for multiple Paf1 complex subunits. We conclude that the Cdc73 C-domain probably constitutes a protein interaction surface that functions with Rtf1 in coupling the Paf1 complex to the RNA polymerase II elongation machinery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The recruitment of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Paf1 complex to active genes requires a domain of Rtf1 that directly interacts with the Spt4-Spt5 complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;33(16):3259-73. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00270-13. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23775116 Free PMC article.
-
Small region of Rtf1 protein can substitute for complete Paf1 complex in facilitating global histone H2B ubiquitylation in yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 3;109(27):10837-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1116994109. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22699496 Free PMC article.
-
Rtf1 is a multifunctional component of the Paf1 complex that regulates gene expression by directing cotranscriptional histone modification.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Sep;27(17):6103-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00772-07. Epub 2007 Jun 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17576814 Free PMC article.
-
The Paf1 complex: platform or player in RNA polymerase II transcription?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 May-Jun;1799(5-6):379-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20060942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Insights into the Roles of the Paf1 Complex in Gene Regulation.Trends Biochem Sci. 2017 Oct;42(10):788-798. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28870425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Casein Kinase 1δ Stabilizes Mature Axons by Inhibiting Transcription Termination of Ankyrin.Dev Cell. 2020 Jan 6;52(1):88-103.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.12.005. Dev Cell. 2020. PMID: 31910362 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN1) Phenocopy Due to a Cell Cycle Division 73 (CDC73) Variant.J Endocr Soc. 2020 Sep 26;4(11):bvaa142. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa142. eCollection 2020 Nov 1. J Endocr Soc. 2020. PMID: 33150274 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Degradation of RNA Polymerase II-Association Factor 1(PAF1) Is Controlled by CNOT4 and 26S Proteasome.PLoS One. 2015 May 1;10(5):e0125599. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125599. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25933433 Free PMC article.
-
Spt6 directly interacts with Cdc73 and is required for Paf1 complex occupancy at active genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jun 9;51(10):4814-4830. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad180. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36928138 Free PMC article.
-
The recruitment of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Paf1 complex to active genes requires a domain of Rtf1 that directly interacts with the Spt4-Spt5 complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;33(16):3259-73. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00270-13. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23775116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wade P. A., Werel W., Fentzke R. C., Thompson N. E., Leykam J. F., Burgess R. R., Jaehning J. A., Burton Z. F. (1996) A novel collection of accessory factors associated with yeast RNA polymerase II. Protein Expr. Purif. 8, 85–90 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

