Somatosensory scaffolding structures
- PMID: 22291616
- PMCID: PMC3263476
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00002
Somatosensory scaffolding structures
Abstract
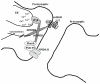
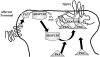
Dynamic changes in somatosensory perception occur as a result of multiple signaling events. In many instances, over-activation of sensory receptors results in the desensitization and subsequent increased threshold for activation of receptors. In other cases, receptor sensitization can occur following tissue injury and/or inflammation. In both cases, signaling mechanisms that control alterations in receptor activities can significantly affect organism response to sensory stimuli, including thermal, mechanical, and chemical. Due to the homeostatic nature of somatosensory recognition, dynamic changes in receptor response can negatively affect an individual's way of life, as well as alert individuals to tissue damage. Here, we will focus on scaffolding structures that regulate somatosensory neuronal excitability.
Keywords: AKAP; Jeske; afferent; homer; lipid raft; pain; scaffold.
Figures
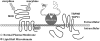
Similar articles
-
Optogenetic Inhibition of CGRPα Sensory Neurons Reveals Their Distinct Roles in Neuropathic and Incisional Pain.J Neurosci. 2018 Jun 20;38(25):5807-5825. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3565-17.2018. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29925650 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of synaptic scaffolding protein Homer 1b/c attenuates secondary hyperalgesia induced by complete Freund's adjuvant in rats.Anesth Analg. 2011 Dec;113(6):1501-8. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31822c0b98. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Anesth Analg. 2011. PMID: 22003220
-
Central sensitization: a generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity.J Pain. 2009 Sep;10(9):895-926. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2009.06.012. J Pain. 2009. PMID: 19712899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of sensory behavioral tasks on pain threshold and cortical excitability.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e52968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052968. Epub 2013 Jan 3. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23301010 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Molecular and cellular limits to somatosensory specificity.Mol Pain. 2008 Apr 18;4:14. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-4-14. Mol Pain. 2008. PMID: 18419827 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nociceptor Translational Profiling Reveals the Ragulator-Rag GTPase Complex as a Critical Generator of Neuropathic Pain.J Neurosci. 2019 Jan 16;39(3):393-411. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2661-18.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 20. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30459229 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the Cl- channel ANO1 by localized calcium signals in nociceptive sensory neurons requires coupling with the IP3 receptor.Sci Signal. 2013 Aug 27;6(290):ra73. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004184. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23982204 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Ca(2+) -activated Cl(-) channel ANO1 by localized Ca(2+) signals.J Physiol. 2016 Jan 1;594(1):19-30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.275107. Epub 2014 Dec 15. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 25398532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local Ca2+ signals couple activation of TRPV1 and ANO1 sensory ion channels.Sci Signal. 2020 Apr 28;13(629):eaaw7963. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaw7963. Sci Signal. 2020. PMID: 32345727 Free PMC article.
-
Inferiority complex: why do sensory ion channels multimerize?Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Feb 28;50(1):213-222. doi: 10.1042/BST20211002. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 35166323 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bregman D. B., Hirsch A. H., Rubin C. S. (1991). Molecular characterization of bovine brain P75, a high affinity binding protein for the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II beta. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 7207–7213 - PubMed
-
- Carr D. W., Stofko-Hahn R. E., Fraser I. D., Cone R. D., Scott J. D. (1992). Localization of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase to the postsynaptic densities by A-kinase anchoring proteins. Characterization of AKAP 79. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 16816–16823 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

