Computational analysis of novel drugs designed for use as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and histamine H3 receptor antagonists for Alzheimer's disease by docking, scoring and de novo evolution
- PMID: 22267207
- PMCID: PMC3493073
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2012.757
Computational analysis of novel drugs designed for use as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and histamine H3 receptor antagonists for Alzheimer's disease by docking, scoring and de novo evolution
Abstract
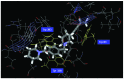
Alzheimer's disease (AD) was first described by Alois Alzheimer in 1907. AD is the most prevalent dementia- related disease, affecting over 20 million individuals worldwide. Currently, however, only a handful of drugs are available and they are at best only able to offer some relief of symptoms. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors, antioxidants, metal chelators, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, anti-inflammatory drugs and NMDA inhibitors are usually used to attempt to cure this disease. AChE inhibitors are the most effective therapy for AD at present. Researchers have found that histamine H3 receptor antagonists decrease re-uptake of acetylcholine and the nervous transmitter substance acetylcholine increases. In this study, we designed compounds by using docking, de novo evolution and adsorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADMET) analysis to AChE inhibitors as well as histamine H3 receptor antagonists to forward drug research and investigate the potent compounds which can pass through the blood-brain barrier. The novel drugs may be useful for the treatment of AD, based on the results of this theoretical calculation study. We will subsequently examine them in future experiments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis, biological evaluation, and computational studies of Tri- and tetracyclic nitrogen-bridgehead compounds as potent dual-acting AChE inhibitors and hH3 receptor antagonists.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Mar 19;5(3):225-42. doi: 10.1021/cn4002126. Epub 2014 Jan 14. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24422467 Free PMC article.
-
Search for new multi-target compounds against Alzheimer's disease among histamine H3 receptor ligands.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Jan 1;185:111785. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111785. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31669851
-
Rational design of new multitarget histamine H3 receptor ligands as potential candidates for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Dec 1;207:112743. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112743. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32882609
-
Dual-target inhibitors based on acetylcholinesterase: Novel agents for Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Dec 5;279:116810. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116810. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39243456 Review.
-
A molecular approach in drug development for Alzheimer's disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:553-565. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.147. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29990843 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacophore-based virtual screening of ZINC database, molecular modeling and designing new derivatives as potential HDAC6 inhibitors.Mol Divers. 2023 Oct;27(5):2053-2071. doi: 10.1007/s11030-022-10540-3. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Mol Divers. 2023. PMID: 36214962
-
Histamine H3 Inverse Agonist BF 2649 or Antagonist with Partial H4 Agonist Activity Clobenpropit Reduces Amyloid Beta Peptide-Induced Brain Pathology in Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jan;55(1):312-321. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0743-8. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28861757
-
Procognitive properties of drugs with single and multitargeting H3 receptor antagonist activities.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014 Jul;20(7):613-23. doi: 10.1111/cns.12279. Epub 2014 May 19. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014. PMID: 24836924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutics of Neurotransmitters in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;57(4):1049-1069. doi: 10.3233/JAD-161118. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28211810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histamine H3 receptor antagonists/inverse agonists on cognitive and motor processes: relevance to Alzheimer's disease, ADHD, schizophrenia, and drug abuse.Front Syst Neurosci. 2012 Oct 23;6:72. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2012.00072. eCollection 2012. Front Syst Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23109919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dorronsoro C, Barbero S, Llorente L, Marcos S. On-eye measurement of optical performance of rigid gas permeable contact lenses based on ocular and corneal aberrometry. Optom Vis Sci. 2003;80:115–125. - PubMed
-
- Guo T, Hobbs DW. Development of BACE1 inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13:1811–1829. - PubMed
-
- Wood KE, Becker BN, McCartney JG, D'Alessandro AM, Coursin DB. Care of the potential organ donor. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2730–2739. - PubMed
-
- Mori F, Fukaya M, Abe H, Wakabayashi K, Watanabe M. Developmental changes in expression of the three ryanodine receptor mRNAs in the mouse brain. Neurosci Lett. 2000;285:57–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

