microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer by targeting PTEN
- PMID: 22267008
- PMCID: PMC3583594
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2012.1645
microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer by targeting PTEN
Abstract
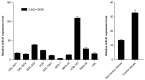
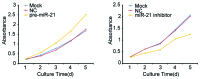
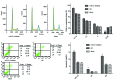
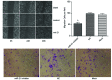
Gastric cancer is one of the most common carcinomas in China. microRNAs, a type of non-coding RNA, are important specific regulators and are involved in numerous bioprocesses of an organism. microRNA-21 (miR-21) has been identified as the most suitable choice for further investigation because it is overexpressed in nearly all solid tumors; furthermore, it has been demonstrated that miR-21 is involved in the genesis and progression of human cancer. It has been reported that PTEN, an important tumour suppressor, is regulated by multiple miRNAs. Thus, in this study we focused on the expression and significance of miR-21 in gastric cancer tissues, and the role of miR-21 in the biological behaviour and the expression of PTEN in gastric cancer cells. Real-time PCR was used to detect miR-21 expression in gastric cancer tissues, the adjacent normal tissues, and the gastric cell lines. The gastric cancer cell line BGC-823 was transfected with pre-miR-21/miR-21 inhibitor to overexpress/downregulate miR-21. The influence of miR-21 on the biological behaviour of gastric cancer cells was evaluated using the CCK-8 kit, FCMs, the scratch healing assay and the transwell test. Western blotting and the Luciferase Reporter Assay were used to evaluate the change of PTEN expression after lowered expression of miR-21 in gastric cancer cell lines. Real-time PCR analysis indicated that miR-21 exhibited higher expression in gastric cancer tissues compared to the adjacent non-tumor tissues. miR-21 expression was significantly associated with the degree of differentiation of the tumour tissues (P=0.004), as well as local invasion and lymph node metastasis (P<0.01). After transfection, pre-miR21 BGC-823 cells grew faster than the negative and control groups (P<0.01). The reduction in miR-21 expression demonstrated a remarkable effect on the biological behaviour of gastric cancer cells (P<0.05); the pre-miR-21-transfected cells healed more quickly compared to the control cells in the scratch healing assay, whereas the transwell test indicated that cell migration in vitro was notably inhibited with the downregulation of miR-21 (P<0.05). The western blot results and Luciferase Reporter Assay demonstrated that PTEN expression was remarkably increased after miR-21 inhibition (P<0.05). microRNA-21 expression was upregulated in gastric carcinoma tissues and was significantly associated with the degree of differentiation of tumour tissues, local invasion and lymph node metastasis. Overexpression of miR-21 promoted BGC-823 cell growth, invasion and cell migration in vitro, whereas downregulation of miR-21 exhibited a stronger inhibitory effect on the biological behaviour of gastric cancer cells; additionally, miR-21 inhibition may upregulate the PTEN expression level, which indicates that PTEN may be a target gene for gastric cancer initiation and development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-17-5p Inhibits the Proliferation and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting PTEN Protein.Altern Ther Health Med. 2022 Nov;28(8):23-29. Altern Ther Health Med. 2022. PMID: 35839114
-
[Role of miR-155 in invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;38(2):86-92. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2016.02.002. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26899325 Chinese.
-
miR-4295 Promotes the Malignant Progression of Gastric Cancer via Targeting PTEN.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(11):1897-1906. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666211110095307. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 34758714
-
MiR-132 promotes the proliferation, invasion and migration of human pancreatic carcinoma by inhibition of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019 Nov;148:65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.09.019. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 28941804 Review.
-
Apoptosis and the target genes of microRNA-21.Chin J Cancer. 2011 Jun;30(6):371-80. doi: 10.5732/cjc.011.10132. Chin J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21627859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-561 inhibits gastric cancercell proliferation and invasion by downregulating c-Myc expression.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Sep 15;8(9):3802-3811. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27725860 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-663b promotes cell proliferation and epithelial mesenchymal transition by directly targeting SMAD7 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Oct;16(4):3129-3134. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6576. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30250517 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of miRNAs in esophageal cancer contributes to radioresistance and limits efficacy of therapy.Biochimie. 2019 Jan;156:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Biochimie. 2019. PMID: 30326253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Novel Phosphatase Domain Mutations Q171R and Y65S Switch PTEN from Tumor Suppressor to Oncogene.Cells. 2021 Dec 5;10(12):3423. doi: 10.3390/cells10123423. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943931 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative miRNA Expression Profile Analysis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Peritumoral Mucosa from the Meso- and Hypopharynx.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017 Jul-Aug;14(4):285-292. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20039. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28647702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Hornstein E, Mansfield JH, Yekta S, et al. The microRNA miR-196 acts upstream of Hoxb8 and Shh in limb development. Nature. 2005;438:671–674. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y, Samal E, Srivastava D. Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature. 2004;436:214–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

