Primordial soup or vinaigrette: did the RNA world evolve at acidic pH?
- PMID: 22264281
- PMCID: PMC3372908
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6150-7-4
Primordial soup or vinaigrette: did the RNA world evolve at acidic pH?
Abstract
Background: The RNA world concept has wide, though certainly not unanimous, support within the origin-of-life scientific community. One view is that life may have emerged as early as the Hadean Eon 4.3-3.8 billion years ago with an atmosphere of high CO(2) producing an acidic ocean of the order of pH 3.5-6. Compatible with this scenario is the intriguing proposal that life arose within alkaline (pH 9-11) deep-sea hydrothermal vents like those of the 'Lost City', with the interface with the acidic ocean creating a proton gradient sufficient to drive the first metabolism. However, RNA is most stable at pH 4-5 and is unstable at alkaline pH, raising the possibility that RNA may have first arisen in the acidic ocean itself (possibly near an acidic hydrothermal vent), acidic volcanic lake or comet pond. As the Hadean Eon progressed, the ocean pH is inferred to have gradually risen to near neutral as atmospheric CO(2) levels decreased.
Presentation of the hypothesis: We propose that RNA is well suited for a world evolving at acidic pH. This is supported by the enhanced stability at acidic pH of not only the RNA phosphodiester bond but also of the aminoacyl-(t)RNA and peptide bonds. Examples of in vitro-selected ribozymes with activities at acid pH have recently been documented. The subsequent transition to a DNA genome could have been partly driven by the gradual rise in ocean pH, since DNA has greater stability than RNA at alkaline pH, but not at acidic pH.
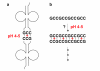
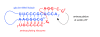
Testing the hypothesis: We have proposed mechanisms for two key RNA world activities that are compatible with an acidic milieu: (i) non-enzymatic RNA replication of a hemi-protonated cytosine-rich oligonucleotide, and (ii) specific aminoacylation of tRNA/hairpins through triple helix interactions between the helical aminoacyl stem and a single-stranded aminoacylating ribozyme.
Implications of the hypothesis: Our hypothesis casts doubt on the hypothesis that RNA evolved in the vicinity of alkaline hydrothermal vents. The ability of RNA to form protonated base pairs and triples at acidic pH suggests that standard base pairing may not have been a dominant requirement of the early RNA world.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primordial ocean chemistry and its compatibility with the RNA world.Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2011 Dec;41(6):553-8. doi: 10.1007/s11084-011-9250-5. Epub 2011 Dec 3. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2011. PMID: 22139511
-
An origin-of-life reactor to simulate alkaline hydrothermal vents.J Mol Evol. 2014 Dec;79(5-6):213-27. doi: 10.1007/s00239-014-9658-4. Epub 2014 Nov 27. J Mol Evol. 2014. PMID: 25428684 Free PMC article.
-
The "Origin-of-Life Reactor" and Reduction of CO2 by H2 in Inorganic Precipitates.J Mol Evol. 2017 Aug;85(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s00239-017-9805-9. Epub 2017 Aug 1. J Mol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28765990 Review.
-
A potential role for RNA aminoacylation prior to its role in peptide synthesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 27;121(35):e2410206121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410206121. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39178230 Free PMC article.
-
Natural pH Gradients in Hydrothermal Alkali Vents Were Unlikely to Have Played a Role in the Origin of Life.J Mol Evol. 2016 Aug;83(1-2):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s00239-016-9756-6. Epub 2016 Aug 17. J Mol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27534947 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-Molecular Dissection of Liquid-Liquid Phase Transitions.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 Aug 9;145(31):17143-17150. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c03812. Epub 2023 Jul 26. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 37494702 Free PMC article.
-
The emergence of DNA in the RNA world: an in silico simulation study of genetic takeover.BMC Evol Biol. 2015 Dec 7;15:272. doi: 10.1186/s12862-015-0548-1. BMC Evol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26643199 Free PMC article.
-
Macrobiont: Cradle for the Origin of Life and Creation of a Biosphere.Life (Basel). 2020 Nov 12;10(11):278. doi: 10.3390/life10110278. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33198206 Free PMC article.
-
Spark of Life: Role of Electrotrophy in the Emergence of Life.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;13(2):356. doi: 10.3390/life13020356. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double Hydrogen Bonding between Side Chain Carboxyl Groups in Aqueous Solutions of Poly (β-L-Malic Acid): Implication for the Evolutionary Origin of Nucleic Acids.Life (Basel). 2017 Aug 28;7(3):35. doi: 10.3390/life7030035. Life (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29061955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morse JW, Mackenzie FT. Hadean ocean carbonate geochemistry. Aquat Geochem. 1998;4:301–319. doi: 10.1023/A:1009632230875. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

