Characterization of glioma stem cells through multiple stem cell markers and their specific sensitization to double-strand break-inducing agents by pharmacological inhibition of ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein
- PMID: 22257080
- PMCID: PMC8057648
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2012.00566.x
Characterization of glioma stem cells through multiple stem cell markers and their specific sensitization to double-strand break-inducing agents by pharmacological inhibition of ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein
Abstract
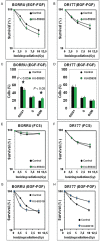
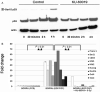
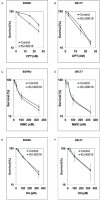
Previous studies have shown that tumor-driving glioma stem cells (GSC) may promote radio-resistance by constitutive activation of the DNA damage response started by the ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) protein. We have investigated whether GSC may be specifically sensitized to ionizing radiation by inhibiting the DNA damage response. Two grade IV glioma cell lines (BORRU and DR177) were characterized for a number of immunocytochemical, karyotypic, proliferative and differentiative parameters. In particular, the expression of a panel of nine stem cell markers was quantified by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and flow cytometry. Overall, BORRU and DR177 displayed pronounced and poor stem phenotypes, respectively. In order to improve the therapeutic efficacy of radiation on GSC, the cells were preincubated with a nontoxic concentration of the ATM inhibitors KU-55933 and KU-60019 and then irradiated. BORRU cells were sensitized to radiation and radio-mimetic chemicals by ATM inhibitors whereas DR177 were protected under the same conditions. No sensitization was observed after cell differentiation or to drugs unable to induce double-strand breaks (DSB), indicating that ATM inhibitors specifically sensitize glioma cells possessing stem phenotype to DSB-inducing agents. In conclusion, pharmacological inhibition of ATM may specifically sensitize GSC to DSB-inducing agents while sparing nonstem cells.
© 2012 The Authors; Brain Pathology © 2012 International Society of Neuropathology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of the phosphorylation of ATM contributes to radioresistance of glioma stem cells.Oncol Rep. 2013 Oct;30(4):1793-801. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2614. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23846672
-
Delayed formation of FancD2 foci in glioma stem cells treated with ionizing radiation.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012 May;138(5):897-9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-012-1217-z. Epub 2012 Apr 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22484854
-
Phenotypic Analysis of ATM Protein Kinase in DNA Double-Strand Break Formation and Repair.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1599:317-334. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6955-5_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28477129
-
ATM: the protein encoded by the gene mutated in the radiosensitive syndrome ataxia-telangiectasia.Int J Radiat Biol. 1999 Oct;75(10):1201-14. doi: 10.1080/095530099139359. Int J Radiat Biol. 1999. PMID: 10549596 Review.
-
Ataxia-telangiectasia-like disorder (ATLD)-its clinical presentation and molecular basis.DNA Repair (Amst). 2004 Aug-Sep;3(8-9):1219-25. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.04.009. DNA Repair (Amst). 2004. PMID: 15279810 Review.
Cited by
-
Disruption of NBS1/MRN Complex Formation by E4orf3 Supports NF-κB That Licenses E1B55K-Deleted Adenovirus-Infected Cells to Accumulate DNA>4n.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0188121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01881-21. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35019694 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitization of orthotopic GIC-driven glioblastoma by doxycycline causes skin damage.Radiat Oncol. 2019 Apr 8;14(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1266-4. Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30961616 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Targets in Diffuse Midline Gliomas-An Emerging Landscape.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 13;13(24):6251. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246251. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA damage response revisited: the p53 family and its regulators provide endless cancer therapy opportunities.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Oct;54(10):1658-1669. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00863-4. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36207426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATM, ATR, CHK1, CHK2 and WEE1 inhibitors in cancer and cancer stem cells.Medchemcomm. 2016 Nov 30;8(2):295-319. doi: 10.1039/c6md00439c. eCollection 2017 Feb 1. Medchemcomm. 2016. PMID: 30108746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arienti KL, Brunmark A, Axe FU, McClure K, Lee A, Blevitt J et al (2005) Checkpoint kinase inhibitors: SAR and radioprotective properties of a series of 2‐arylbenzimidazoles. J Med Chem 48:1873–1885. - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB et al (2006) Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444:756–760. - PubMed
-
- Bolderson E, Richard DJ, Zhou BB, Khanna KK (2009) Recent advances in cancer therapy targeting proteins involved in DNA double‐strand break repair. Clin Cancer Res 15:6314–6320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

