A 4-trifluoromethyl analogue of celecoxib inhibits arthritis by suppressing innate immune cell activation
- PMID: 22251404
- PMCID: PMC3392797
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3683
A 4-trifluoromethyl analogue of celecoxib inhibits arthritis by suppressing innate immune cell activation
Abstract
Introduction: Celecoxib, a highly specific cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor has been reported to have COX-2-independent immunomodulatory effects. However, celecoxib itself has only mild suppressive effects on arthritis. Recently, we reported that a 4-trifluoromethyl analogue of celecoxib (TFM-C) with 205-fold lower COX-2-inhibitory activity inhibits secretion of IL-12 family cytokines through a COX-2-independent mechanism that involves Ca2+-mediated intracellular retention of the IL-12 polypeptide chains. In this study, we explored the capacity of TFM-C as a new therapeutic agent for arthritis.
Methods: To induce collagen-induced arthritis (CIA), DBA1/J mice were immunized with bovine type II collagen (CII) in Freund's adjuvant. Collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) was induced in C57BL/6 mice by injecting anti-CII antibodies. Mice received 10 μg/g of TFM-C or celecoxib every other day. The effects of TFM-C on clinical and histopathological severities were assessed. The serum levels of CII-specific antibodies were measured by ELISA. The effects of TFM-C on mast cell activation, cytokine producing capacity by macrophages, and neutrophil recruitment were also evaluated.
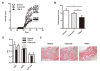
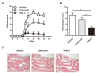
Results: TFM-C inhibited the severity of CIA and CAIA more strongly than celecoxib. TFM-C treatments had little effect on CII-specific antibody levels in serum. TFM-C suppressed the activation of mast cells in arthritic joints. TFM-C also suppressed the production of inflammatory cytokines by macrophages and leukocyte influx in thioglycollate-induced peritonitis.
Conclusion: These results indicate that TFM-C may serve as an effective new disease-modifying drug for treatment of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures

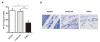
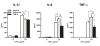
Similar articles
-
Mucosal-associated invariant T cells promote inflammation and exacerbate disease in murine models of arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Jan;64(1):153-61. doi: 10.1002/art.33314. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 21904999
-
Torilin ameliorates type II collagen-induced arthritis in mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Jun;16(2):232-42. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.04.012. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23623942
-
Immunization with TCR Vbeta10 peptide reduces the frequency of type-II collagen-specific Th1 type T cells in BUB/BnJ (H-2q) mice.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2001 Jul-Aug;19(4):385-94. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11491493
-
c-Fms-mediated differentiation and priming of monocyte lineage cells play a central role in autoimmune arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(1):R32. doi: 10.1186/ar2940. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20181277 Free PMC article.
-
Oral administration of type-II collagen peptide 250-270 suppresses specific cellular and humoral immune response in collagen-induced arthritis.Clin Immunol. 2007 Jan;122(1):75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.08.004. Epub 2006 Oct 11. Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17045846
Cited by
-
Urokinase plasminogen activator and receptor promote collagen-induced arthritis through expression in hematopoietic cells.Blood Adv. 2017 Mar 21;1(9):545-556. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2016004002. eCollection 2017 Mar 28. Blood Adv. 2017. PMID: 29296974 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells in Autoimmune Diseases.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 11;9:1333. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01333. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29942318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multiplex immunoassay method for simultaneous quantification of iron, vitamin A and inflammation status markers.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 19;9(12):e115164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115164. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25525806 Free PMC article.
-
Improved serological detection of rheumatoid arthritis: a highly antigenic mimotope of carbonic anhydrase III selected in a murine model by phage display.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Jun 23;17(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0685-3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26099944 Free PMC article.
-
A trifluoromethyl analogue of celecoxib exerts beneficial effects in neuroinflammation.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 11;8(12):e83119. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083119. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishimoto N, Yoshizaki K, Miyasaka N, Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, Hashimoto J, Azuma J, Kishimoto T. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody: a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1761–1769. doi: 10.1002/art.20303. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maini RN, Taylor PC, Szechinski J, Pavelka K, Bröll J, Balint G, Emery P, Raemen F, Petersen J, Smolen J, Thomson D, Kishimoto T. CHARISMA Study Group. Double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, tocilizumab, in European patients with rheumatoid arthritis who had an incomplete response to methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2817–2829. doi: 10.1002/art.22033. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

